Index
Rasters.RastersRasters.AbstractProjectedRasters.AbstractRasterRasters.AbstractRasterSeriesRasters.AbstractRasterStackRasters.BandRasters.FileArrayRasters.FileStackRasters.MappedRasters.OpenStackRasters.ProjectedRasters.RasterRasters.RasterDiskArrayRasters.RasterSeriesRasters.RasterStackRasters.SourceRasters.aggregateRasters.aggregate!Rasters.boolmaskRasters.cellareaRasters.checkmem!Rasters.classifyRasters.classify!Rasters.combineRasters.convertlookupRasters.coverageRasters.coverage!Rasters.createRasters.cropRasters.disaggregateRasters.disaggregate!Rasters.extendRasters.extractRasters.mappedboundsRasters.mappedcrsRasters.mappedindexRasters.maskRasters.mask!Rasters.missingmaskRasters.missingvalRasters.mosaicRasters.mosaic!Rasters.pointsRasters.rasterizeRasters.rasterize!Rasters.replace_missingRasters.reprojectRasters.reprojectRasters.resampleRasters.rplotRasters.rplotRasters.sampleRasters.setcrsRasters.setmappedcrsRasters.sliceRasters.trimRasters.warpRasters.zonal
Reference - Exported functions
Rasters.Rasters Module
sourceRasters.AbstractRaster Type
AbstractRaster <: DimensionalData.AbstractDimArrayAbstract supertype for objects that wrap an array (or location of an array) and metadata about its contents. It may be memory or hold a FileArray, which holds the filename, and is only opened when required.
AbstractRasters inherit from AbstractDimArray from DimensionalData.jl. They can be indexed as regular Julia arrays or with DimensionalData.jl Dimensions. They will plot as a heatmap in Plots.jl with correct coordinates and labels, even after slicing with getindex or view. getindex on a AbstractRaster will always return a memory-backed Raster.
Rasters.AbstractRasterSeries Type
AbstractRasterSeries <: DimensionalData.AbstractDimensionalArrayAbstract supertype for high-level DimensionalArray that hold RasterStacks, Rasters, or the paths they can be loaded from. RasterSeries are indexed with dimensions as with a AbstractRaster. This is useful when you have multiple files containing rasters or stacks of rasters spread over dimensions like time and elevation.
As much as possible, implementations should facilitate loading entire directories and detecting the dimensions from metadata.
This allows syntax like below for a series of stacks of arrays:
RasterSeries[Time(Near(DateTime(2001, 1))][:temp][Y(Between(70, 150)), X(Between(-20,20))] |> plot`RasterSeries is the concrete implementation.
Rasters.AbstractRasterStack Type
AbstractRasterStackAbstract supertype for objects that hold multiple AbstractRasters that share spatial dimensions.
They are NamedTuple-like structures that may either contain NamedTuple of AbstractRasters, string paths that will load AbstractRasters, or a single path that points to a file containing multiple layers, like NetCDF or HDF5. Use and syntax is similar or identical for all cases.
AbstractRasterStack can hold layers that share some or all of their dimensions. They cannot have the same dimension with different length or spatial extent as another layer.
getindex on an AbstractRasterStack generally returns a memory backed standard Raster. raster[:somelayer] |> plot plots the layers array, while raster[:somelayer, X(1:100), Band(2)] |> plot will plot the subset without loading the whole array.
getindex on an AbstractRasterStack with a key returns another stack with getindex applied to all the arrays in the stack.
Rasters.Band Type
Band <: Dimension
Band(val=:)Band Dimension for multi-band rasters.
Example:
banddim = Band(10:10:100)
# Or
val = A[Band(1)]
# Or
mean(A; dims=Band)Rasters.Mapped Type
Mapped <: AbstractProjected
Mapped(order, span, sampling, crs, mappedcrs)
Mapped(; order=AutoOrder(), span=AutoSpan(), sampling=AutoSampling(), crs=nothing, mappedcrs)An AbstractSampled Lookup, where the dimension index has been mapped to another projection, usually lat/lon or EPSG(4326). Mapped matches the dimension format commonly used in netcdf files.
Fields and behaviours are identical to Sampled with the addition of crs and mappedcrs fields.
The mapped dimension index will be used as for Sampled, but to save in another format the underlying crs may be used to convert it.
Rasters.Projected Type
Projected <: AbstractProjected
Projected(order, span, sampling, crs, mappedcrs)
Projected(; order=AutoOrder(), span=AutoSpan(), sampling=AutoSampling(), crs, mappedcrs=nothing)An AbstractSampled Lookup with projections attached.
Fields and behaviours are identical to Sampled with the addition of crs and mappedcrs fields.
If both crs and mappedcrs fields contain CRS data (in a GeoFormat wrapper from GeoFormatTypes.jl) the selector inputs and plot axes will be converted from and to the specified mappedcrs projection automatically. A common use case would be to pass mappedcrs=EPSG(4326) to the constructor when loading eg. a GDALarray:
GDALarray(filename; mappedcrs=EPSG(4326))The underlying crs will be detected by GDAL.
If mappedcrs is not supplied (ie. mappedcrs=nothing), the base index will be shown on plots, and selectors will need to use whatever format it is in.
Rasters.Raster Type
Raster <: AbstractRaster
Raster(filepath::String; kw...)
Raster(A::AbstractDimArray; kw...)
Raster(A::AbstractArray, dims; kw...)A generic AbstractRaster for spatial/raster array data. It can hold either memory-backed arrays or, if lazy=true, a FileArray, which stores the String path to an unopened file.
If lazy=true, the file will only be opened lazily when it is indexed with getindex or when read(A) is called. Broadcasting, taking a view, reversing, and most other methods will not load data from disk; they will be applied later, lazily.
Arguments
dims:TupleofDimensions needed when anAbstractArrayis used.
Keywords
name: aSymbolname for a Raster, which will also retrieve the a named layer ifRasteris used on a multi-layered file like a NetCDF.group: the group in the dataset wherenamecan be found. Only needed for nested datasets. AStringorSymbolwill select a single group. Pairs can also used to access groups at any nested depth, i.egroup=:group1 => :group2 => :group3.missingval: value representing missing data, normally detected from the file and automatically converted tomissing. Setting to an alternate value, such as0orNaNmay be desirable for improved perfomance.nothingspecifies no missing value. Using the samemissingvalthe file already has removes the overhead of replacing it, this can be done by passing themissingvalfunction asmissingval. If the file has an incorrect value, we can manually define the transformation as a pair likecorrect_value => missingorcorrect_value => NaN.correct_value => correct_valuewill keep remove the overhead of changing it. Note: Whenraw=trueis set,missingvalis not changed from the value specified in the file.metadata:DictorMetadataobject for the array, orNoMetadata().crs: the coordinate reference system of the objectsXDim/YDimdimensions. Only set this if you know the detected crs is incorrect, or it is not present in the file. Thecrsis expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jlCRSorMixedmodeGeoFormatobject, likeEPSG(4326).mappedcrs: the mapped coordinate reference system of the objectsXDim/YDimdimensions. forMappedlookups these are the actual values of the index. ForProjectedlookups this can be used to index in eg.EPSG(4326)lat/lon values, having it converted automatically. Only set this if the detectedmappedcrsin incorrect, or the file does not have amappedcrs, e.g. a tiff. Themappedcrsis expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jlCRSorMixedmodeGeoFormattype.refdims:Tuple ofpositionDimensions the array was sliced from, defaulting to(). Usually not needed.
When a filepath String is used:
dropband: drop single band dimensions when creating stacks from filenames.trueby default.lazy: ABoolspecifying if to load data lazily from disk.falseby default.source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.scaled: apply scale and offset asx * scale + offsetwherescaleand/oroffsetare found in file metadata.trueby default. This is common where data has been convert to e.g. UInt8 to save disk space. To ignorescaleandoffsetmetadata, usescaled=false. Note 1: Ifscaleandoffsetare1.0and0.0they will be ignored and the original type will be used even whenscaled=true. This is because these values may be fallback defaults and we do not want to convert everyRealarray to largerFloat64values. Note 2:raw=truewill ignorescaledandmissingvaland return the raw values.raw: turn of all scaling and masking and load the raw values from disk.falseby default. Iftrue,scaledwill be set tofalseandmissingvalwill to the existing missing value in the file. A warning will be printed ifscaledormissingvalare manually set to another value.
When A is an AbstractDimArray:
data: can replace the data in an existingAbstractRaster
Rasters.RasterSeries Type
RasterSeries <: AbstractRasterSeries
RasterSeries(rasters::AbstractArray{<:AbstractRaster}, dims; [refdims])
RasterSeries(stacks::AbstractArray{<:AbstractRasterStack}, dims; [refdims])
RasterSeries(paths::AbstractArray{<:AbstractString}, dims; child, duplicate_first, kw...)
RasterSeries(path:::AbstractString, dims; ext, separator, child, duplicate_first, kw...)
RasterSeries(objects::AbstractBasicDimArray; kw...)Concrete implementation of AbstractRasterSeries.
A RasterSeries is an array of Rasters or RasterStacks, along some dimension(s).
Existing Raster RasterStack can be wrapped in a RasterSeries, or new files can be loaded from an array of String or from a single String.
A single String can refer to a whole directory, or the name of a series of files in a directory, sharing a common stem. The differnce between the filenames can be used as the lookup for the series.
For example, with some tifs at these paths :
"series_dir/myseries_2001-01-01T00:00:00.tif"
"series_dir/myseries_2002-01-01T00:00:00.tif"We can load a RasterSeries with a DateTime lookup:
julia> ser = RasterSeries("series_dir/myseries.tif", Ti(DateTime))
2-element RasterSeries{Raster,1} with dimensions:
Ti Sampled{DateTime} DateTime[DateTime("2001-01-01T00:00:00"), DateTime("2002-01-01T00:00:00")] ForwardOrdered Irregular PointsThe DateTime suffix is parsed from the filenames. Using Ti(Int) would try to parse integers instead.
Just using the directory will also work, unless there are other files mixed in it:
julia> ser = RasterSeries("series_dir", Ti(DateTime))
2-element RasterSeries{Raster,1} with dimensions:
Ti Sampled{DateTime} DateTime[DateTime("2001-01-01T00:00:00"), DateTime("2002-01-01T00:00:00")] ForwardOrdered Irregular PointsArguments
dims: series dimension/s.
Keywords
When loading a series from a Vector of String paths or a single String path:
child: constructor of child objects for use when filenames are passed in, can beRasterorRasterStack. Defaults toRaster.duplicate_first::Bool: wether to duplicate the dimensions and metadata of the first file with all other files. This can save load time with a large series where dimensions are identical.falseby default.lazy: ABoolspecifying if to load data lazily from disk.falseby default.kw: keywords passed to the child constructorRasterorRasterStack.
When loading a series from a single String path:
separator: separator used to split lookup elements from the rest of a filename. '_' by default.
Others:
refdims: existing reference dimension/s, normally not required.
Rasters.RasterStack Type
RasterStack <: AbstrackRasterStack
RasterStack(data...; name, kw...)
RasterStack(data::Union{Vector,Tuple}; name, kw...)
RasterStack(data::NamedTuple; kw...))
RasterStack(data::RasterStack; kw...)
RasterStack(data::Raster; layersfrom=Band, kw...)
RasterStack(filepath::AbstractString; kw...)Load a file path or a NamedTuple of paths as a RasterStack, or convert arguments, a Vector or NamedTuple of Rasters to RasterStack.
Arguments
data: ANamedTupleofRasters orString, or aVector,Tupleor splatted arguments ofRaster. The latter options must pass anamekeyword argument.filepath: A file (such as netcdf or tif) to be loaded as a stack, or a directory path containing multiple files.
Keywords
name: Used as stack layer names when aTuple,Vectoror splat ofRasteris passed in. Has no effect whenNameTupleis used - theNamedTuplekeys are the layer names.group: the group in the dataset wherenamecan be found. Only needed for nested datasets. AStringorSymbolwill select a single group. Pairs can also used to access groups at any nested depth, i.egroup=:group1 => :group2 => :group3.metadata: ADictorDimensionalData.Metadataobject.missingval: value representing missing data, normally detected from the file and automatically converted tomissing. Setting to an alternate value, such as0orNaNmay be desirable for improved perfomance.nothingspecifies no missing value. Using the samemissingvalthe file already has removes the overhead of replacing it, this can be done by passing themissingvalfunction asmissingval. If the file has an incorrect value, we can manually define the transformation as a pair likecorrect_value => missingorcorrect_value => NaN.correct_value => correct_valuewill keep remove the overhead of changing it. Note: Whenraw=trueis set,missingvalis not changed from the value specified in the file. ForRasterStackaNamedTuplecan also be passed if layers should have differentmissingval.crs: the coordinate reference system of the objectsXDim/YDimdimensions. Only set this if you know the detected crs is incorrect, or it is not present in the file. Thecrsis expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jlCRSorMixedmodeGeoFormatobject, likeEPSG(4326).mappedcrs: the mapped coordinate reference system of the objectsXDim/YDimdimensions. forMappedlookups these are the actual values of the index. ForProjectedlookups this can be used to index in eg.EPSG(4326)lat/lon values, having it converted automatically. Only set this if the detectedmappedcrsin incorrect, or the file does not have amappedcrs, e.g. a tiff. Themappedcrsis expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jlCRSorMixedmodeGeoFormattype.refdims:TupleofDimensionthat the stack was sliced from.
For when one or multiple filepaths are used:
dropband: drop single band dimensions when creating stacks from filenames.trueby default.lazy: ABoolspecifying if to load data lazily from disk.falseby default.raw: turn of all scaling and masking and load the raw values from disk.falseby default. Iftrue,scaledwill be set tofalseandmissingvalwill to the existing missing value in the file. A warning will be printed ifscaledormissingvalare manually set to another value.scaled: apply scale and offset asx * scale + offsetwherescaleand/oroffsetare found in file metadata.trueby default. This is common where data has been convert to e.g. UInt8 to save disk space. To ignorescaleandoffsetmetadata, usescaled=false. Note 1: Ifscaleandoffsetare1.0and0.0they will be ignored and the original type will be used even whenscaled=true. This is because these values may be fallback defaults and we do not want to convert everyRealarray to largerFloat64values. Note 2:raw=truewill ignorescaledandmissingvaland return the raw values.source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.
For when a single Raster is used:
layersfrom:Dimensionto source stack layers from if the file is not already multi-layered.nothingis default, so that a singleRasterStack(raster)is a single layered stack.RasterStack(raster; layersfrom=Band)will use the bands as layers.
files = (temp="temp.tif", pressure="pressure.tif", relhum="relhum.tif")
stack = RasterStack(files; mappedcrs=EPSG(4326))
stack[:relhum][Lat(Contains(-37), Lon(Contains(144))DimensionalData.modify Method
modify(f, series::AbstractRasterSeries)Apply function f to the data of the child object. If the child is an AbstractRasterStack the function will be passed on to its child AbstractRasters.
f must return an identically sized array.
This method triggers a complete rebuild of all objects, and disk based objects will be transferred to memory.
An example of the usefulnesss of this is for swapping out array backend for an entire series to CuArray from CUDA.jl to copy data to a GPU.
GeoInterface.crs Method
crs(x::Raster)Get the projected coordinate reference system of a Y or X Dimension, or of the Y/X dims of an AbstractRaster.
For Mapped lookup this may be nothing as there may be no projected coordinate reference system at all. See setcrs to set it manually.
Rasters.aggregate Function
aggregate(method, object, scale; kw...)Aggregate a Raster, or all arrays in a RasterStack or RasterSeries, by scale using method.
Arguments
method: a function such asmeanorsumthat can combine the value of multiple cells to generate the aggregated cell, or aLocuslikeStart()orCenter()that species where to sample from in the interval.object: Object to aggregate, likeAbstractRasterSeries,AbstractStack,AbstractRasterorDimension.scale: the aggregation factor, which can be anInt, aTupleofIntfor each dimension, or a:colon to mean the whole dimension. You can also use anyDimension,SelectororIntcombination you can usually use ingetindex.TupleofPairorNamedTuplewhere keys are dimension names will also work. Using aSelectorwill determine the scale by the distance from the start of the index. Selectors will find the first offset and repeat the same aggregation size for the rest.
When the aggregation scale of is larger than the array axis, the length of the axis is used.
Keywords
skipmissing: iftrue, anymissingvalwill be skipped during aggregation, so that only areas of all missing values will be aggregated tomissingval(dst). Iffalse, aggregated areas containing one or moremissingvalwill be assignedmissingval.falseby default.skipmissingbehaviour is independent of functionf, which is only applied to completely non-missing values.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, Statistics, Plots
import ArchGDAL
using Rasters: Center
st = RasterStack(WorldClim{Climate}; month=1)
ag = aggregate(Center(), st, (Y(20), X(20)); skipmissingval=true, progress=false)
plot(ag)
savefig("build/aggregate_example.png"); nothing
# output
Note: currently it is faster to aggregate over memory-backed arrays. Use read on src before use where required.
Rasters.aggregate! Method
aggregate!(method, dst::AbstractRaster, src::AbstractRaster, scale; skipmissing=false)Aggregate raster src to raster dst by scale, using method.
Arguments
method: a function such asmeanorsumthat can combine the value of multiple cells to generate the aggregated cell, or aLocuslikeStart()orCenter()that species where to sample from in the interval.scale: the aggregation factor, which can be anInt, aTupleofIntfor each dimension, or a:colon to mean the whole dimension. You can also use anyDimension,SelectororIntcombination you can usually use ingetindex.TupleofPairorNamedTuplewhere keys are dimension names will also work. Using aSelectorwill determine the scale by the distance from the start of the index. Selectors will find the first offset and repeat the same aggregation size for the rest.
When the aggregation scale of is larger than the array axis, the length of the axis is used.
Keywords
skipmissing: iftrue, anymissingvalwill be skipped during aggregation, so that only areas of all missing values will be aggregated tomissingval(dst). Iffalse, aggregated areas containing one or moremissingvalwill be assignedmissingval.falseby default.skipmissingbehaviour is independent of functionf, which is only applied to completely non-missing values.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.
Note: currently it is much faster to aggregate over memory-backed source arrays. Use read on src before use where required.
Rasters.boolmask Function
boolmask(obj::Raster; [missingval])
boolmask(obj; [to, res, size])
boolmask(obj::RasterStack; alllayers=true, kw...)Create a mask array of Bool values, from another Raster. AbstractRasterStack or AbstractRasterSeries are also accepted.
The array returned from calling boolmask on a AbstractRaster is a Raster with the same dimensions as the original array and a missingval of false.
Arguments
- a
Rasteror one or multiple geometries. Geometries can be a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Raster / RasterStack Keywords
invert: invert the mask, so that areas no missing inwithare masked, and areas missing inwithare masked.missingval: The missing value of the source array, with defaultmissingval(raster).
Keywords
alllayers: iftruea mask is taken for all layers, otherwise only the first layer is used. Defaults totrueto: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.
For tabular data, feature collections and other iterables
collapse: iftrue, collapse all geometry masks into a single mask. Otherwise return a Raster with an additionalgeometrydimension, so that each slice along this axis is the mask of thegeometryopbject of each row of the table, feature in the feature collection, or just each geometry in the iterable.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates
wc = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
boolmask(wc) |> plot
savefig("build/boolmask_example.png"); nothing
# output
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.cellarea Method
cellarea([method], x)Gives the approximate area of each gridcell of x. By assuming the earth is a sphere, it approximates the true size to about 0.1%, depending on latitude.
Run using ArchGDAL or using Proj to make this method fully available.
method: You can specify whether you want to compute the area in the plane of your projectionPlanar()or on a sphere of some radiusSpherical(; radius=...)(the default).Sphericalwill compute cell area on the sphere, by transforming all points back to long-lat. You can specify the radius by theradiuskeyword argument here. By default, this is6371008.8, the mean radius of the Earth.Planarwill compute cell area in the plane of the CRS you have chosen. Be warned that this will likely be incorrect for non-equal-area projections.
Returns a Raster with the same x and y dimensions as the input, where each value in the raster encodes the area of the cell (in meters by default).
Example
using Rasters, Proj, Rasters.Lookups
xdim = X(Projected(90.0:10.0:120; sampling=Intervals(Start()), crs=EPSG(4326)))
ydim = Y(Projected(0.0:10.0:50; sampling=Intervals(Start()), crs=EPSG(4326)))
myraster = rand(xdim, ydim)
cs = cellarea(myraster)
# output
╭───────────────────────╮
│ 4×6 Raster{Float64,2} │
├───────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────── dims ┐
↓ X Projected{Float64} 90.0:10.0:120.0 ForwardOrdered Regular Intervals{Start},
→ Y Projected{Float64} 0.0:10.0:50.0 ForwardOrdered Regular Intervals{Start}
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── raster ┤
extent: Extent(X = (90.0, 130.0), Y = (0.0, 60.0))
crs: EPSG:4326
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓ → 0.0 10.0 20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0
90.0 1.23017e6 1.19279e6 1.11917e6 1.01154e6 873182.0 708290.0
100.0 1.23017e6 1.19279e6 1.11917e6 1.01154e6 873182.0 708290.0
110.0 1.23017e6 1.19279e6 1.11917e6 1.01154e6 873182.0 708290.0
120.0 1.23017e6 1.19279e6 1.11917e6 1.01154e6 873182.0 708290.0WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.classify Function
classify(x, pairs; lower=(>=), upper=(<), others=nothing)
classify(x, pairs...; lower, upper, others)Create a new array with values in x classified by the values in pairs.
pairs can hold tuples fo values (2, 3), a Fix2 function e.g. <=(1), a Tuple of Fix2 e.g. (>=(4), <(7)), or an IntervalSets.jl interval, e.g. 3..9 or OpenInterval(10, 12). pairs can also be a n * 3 matrix where each row is lower bounds, upper bounds, replacement.
If tuples or a Matrix are used, the lower and upper keywords define how the lower and upper boundaries are chosen.
If others is set other values not covered in pairs will be set to that values.
Arguments
x: aRasterorRasterStackpairs: each pair contains a value and a replacement, a tuple of lower and upper range and a replacement, or a Tuple ofFix2like(>(x), <(y).
Keywords
lower: Which comparison (<or<=) to use for lower values, ifFix2are not used.upper: Which comparison (>or>=) to use for upper values, ifFix2are not used.others: A value to assign to all values not included inpairs. Passingnothing(the default) will leave them unchanged.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots
A = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :tavg; month=1)
classes = <=(15) => 10,
15..25 => 20,
25..35 => 30,
>(35) => 40
classified = classify(A, classes; others=0, missingval=0)
plot(classified; c=:magma)
savefig("build/classify_example.png"); nothing
# output
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.classify! Method
classify!(x, pairs...; lower, upper, others)
classify!(x, pairs; lower, upper, others)Classify the values of x in-place, by the values in pairs.
If Fix2 is not used, the lower and upper keywords
If others is set other values not covered in pairs will be set to that values.
Arguments
x: aRasterorRasterStackpairs: each pair contains a value and a replacement, a tuple of lower and upper range and a replacement, or a Tuple ofFix2like(>(x), <(y).
Keywords
lower: Which comparison (<or<=) to use for lower values, ifFix2are not used.upper: Which comparison (>or>=) to use for upper values, ifFix2are not used.others: A value to assign to all values not included inpairs. Passingnothing(the default) will leave them unchanged.
Example
classify! to disk, with key steps:
copying a tempory file so we don't write over the RasterDataSources.jl version.
use
openwithwrite=trueto open the file with disk-write permissions.use
Float32like10.0f0for all our replacement values andother, because the file is stored asFloat32. Attempting to write some other type will fail.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots
# Download and copy the file
filename = getraster(WorldClim{Climate}, :tavg; month=6)
tempfile = tempname() * ".tif"
cp(filename, tempfile)
# Define classes
classes = (5, 15) => 10,
(15, 25) => 20,
(25, 35) => 30,
>=(35) => 40
# Open the file with write permission
open(Raster(tempfile); write=true) do A
classify!(A, classes; others=0)
end
# Open it again to plot the changes
plot(Raster(tempfile); c=:magma)
savefig("build/classify_bang_example.png"); nothing
# output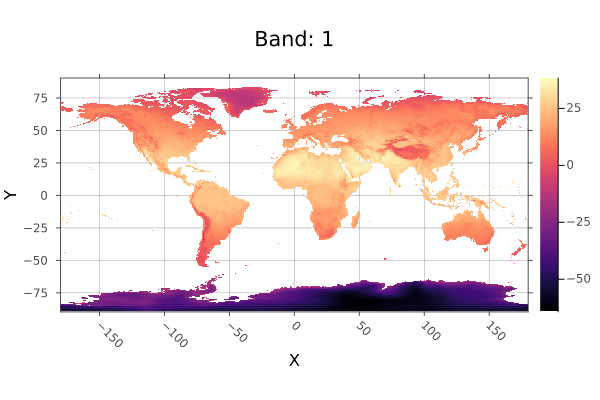
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.combine Method
combine(A::AbstracRasterSeries; [dims], [lazy]) => RasterCombine a RasterSeries along some dimension/s, creating a new Raster or RasterStack, depending on the contents of the series.
If dims are passed, only the specified dimensions will be combined with a RasterSeries returned, unless dims is all the dims in the series.
If lazy, concatenate lazily. The default is to concatenate lazily for lazy Rasters and eagerly otherwise.
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.convertlookup Method
convertlookup(dstlookup::Type{<:Lookup}, x)Convert the dimension lookup between Projected and Mapped. Other dimension lookups pass through unchanged.
This is used to e.g. save a netcdf file to GeoTiff.
sourceRasters.coverage! Method
coverage!(A, geom; [mode, scale])Calculate the area of a raster covered by GeoInterface.jl compatible geometry geom, as a fraction.
Each pixel is assigned a grid of points (by default 10 x 10) that are each checked to be inside the geometry. The sum divided by the number of points to give coverage.
In practice, most pixel coverage is not calculated this way - shortcuts that produce the same result are taken wherever possible.
If geom is an AbstractVector or table, the mode keyword will determine how coverage is combined.
Keywords
mode: method for combining multiple geometries -unionorsum.union(the default) gives the areas covered by all geometries. Usefull in spatial coverage where overlapping regions should not be counted twice. The returned raster will containFloat64values between0.0and1.0.sumgives the summed total of the areas covered by all geometries, as in taking the sum of runningcoverageseparately on all geometries. The returned values are positiveFloat64.
For a single geometry, the
modekeyword has no effect - the result is the same.scale:Integerscale of pixel subdivision. The default of10means each pixel has 10 x 10 or 100 points that contribute to coverage. Using100means 10,000 points contribute. Performance will decline asscaleincreases. Memory use will grow byscale^2whenmode=:union.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.
Rasters.coverage Method
coverage(mode, geom; [to, res, size, scale, verbose, progress])
coverage(geom; [to, mode, res, size, scale, verbose, progress])Calculate the area of a raster covered by GeoInterface.jl compatible geometry geom, as a fraction.
Each pixel is assigned a grid of points (by default 10 x 10) that are each checked to be inside the geometry. The sum divided by the number of points to give coverage.
In practice, most pixel coverage is not calculated this way - shortcuts that produce the same result are taken wherever possible.
If geom is an AbstractVector or table, the mode keyword will determine how coverage is combined.
Keywords
mode: method for combining multiple geometries -unionorsum.union(the default) gives the areas covered by all geometries. Usefull in spatial coverage where overlapping regions should not be counted twice. The returned raster will containFloat64values between0.0and1.0.sumgives the summed total of the areas covered by all geometries, as in taking the sum of runningcoverageseparately on all geometries. The returned values are positiveFloat64.
For a single geometry, the
modekeyword has no effect - the result is the same.scale:Integerscale of pixel subdivision. The default of10means each pixel has 10 x 10 or 100 points that contribute to coverage. Using100means 10,000 points contribute. Performance will decline asscaleincreases. Memory use will grow byscale^2whenmode=:union.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.
Rasters.crop Function
crop(x; to, touches=false, atol=0, [geometrycolumn])
crop(xs...; to)Crop one or multiple AbstractRaster or AbstractRasterStack x to match the size of the object to, or smallest of any dimensions that are shared.
crop is lazy, using a view into the object rather than allocating new memory.
Keywords
to: the object to crop to. This can be aRasteror one or multiple geometries. Geometries can be a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified. If notokeyword is passed, the smallest shared area of allxsis used.touches:trueorfalse. Whether to useToucheswraper on the object extent. When lines need to be included in e.g. zonal statistics,trueshould be used.atol: the absolute tolerance to use when cropping to an extent. If edges are less thanatolaway from the extent ofto, they are included.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.
As crop is lazy, filename and suffix keywords are not used.
Example
Crop to another raster:
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, Plots
evenness = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :evenness)
rnge = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :range)
# Roughly cut out New Zealand from the evenness raster
nz_bounds = X(165 .. 180), Y(-50 .. -32)
nz_evenness = evenness[nz_bounds...]
# Crop range to match evenness
nz_range = crop(rnge; to=nz_evenness)
plot(nz_range)
savefig("build/nz_crop_example.png");
nothing
# output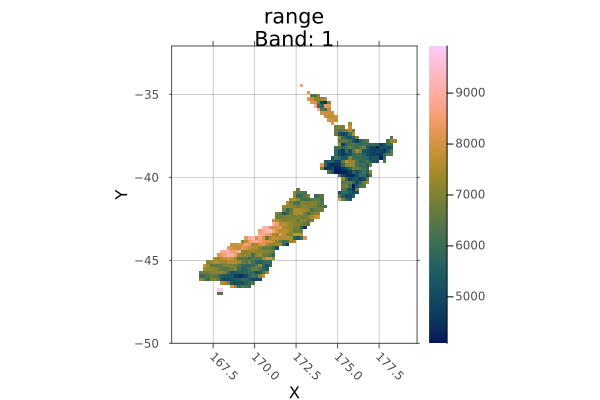
Crop to a polygon:
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, Plots, Dates, Shapefile, Downloads
# Download a borders shapefile
shapefile_url = "https://github.com/nvkelso/natural-earth-vector/raw/master/10m_cultural/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp"
shapefile_name = "boundary.shp"
isfile(shapefile_name) || Downloads.download(shapefile_url, shapefile_name)
shp = Shapefile.Handle(shapefile_name).shapes[6]
evenness = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :evenness)
argentina_evenness = crop(evenness; to=shp)
plot(argentina_evenness)
savefig("build/argentina_crop_example.png"); nothing
# output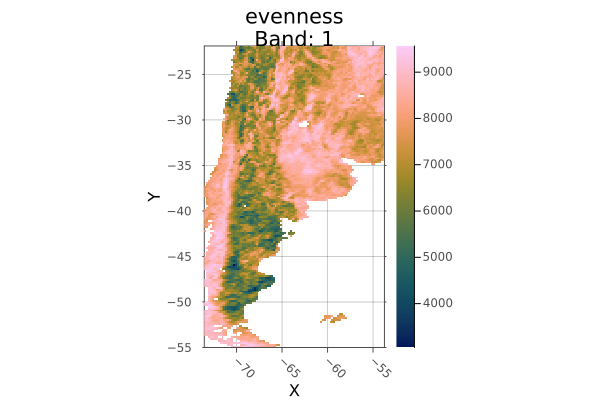
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.disaggregate Function
disaggregate(object, scale; kw...)Disaggregate array, or all arrays in a stack or series, by some scale.
Arguments
object: Object to aggregate, likeAbstractRasterSeries,AbstractStack,AbstractRaster,DimensionorLookup.scale: the aggregation factor, which can be anInt, aTupleofIntfor each dimension, or a:colon to mean the whole dimension. You can also use anyDimension,SelectororIntcombination you can usually use ingetindex.TupleofPairorNamedTuplewhere keys are dimension names will also work. Using aSelectorwill determine the scale by the distance from the start of the index. Selectors will find the first offset and repeat the same aggregation size for the rest.
Keywords
filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.lazy: ABoolspecifying if to disaggregate lazily. Defaults tofalse
Note: currently it is much faster to disaggregate over a memory-backed source array. Use read on src before use where required.
Rasters.disaggregate! Method
disaggregate!(dst::AbstractRaster, src::AbstractRaster, scale)Disaggregate array src to array dst by some scale.
scale: the aggregation factor, which can be anInt, aTupleofIntfor each dimension, or a:colon to mean the whole dimension. You can also use anyDimension,SelectororIntcombination you can usually use ingetindex.TupleofPairorNamedTuplewhere keys are dimension names will also work. Using aSelectorwill determine the scale by the distance from the start of the index. Selectors will find the first offset and repeat the same aggregation size for the rest.
Rasters.extend Function
extend(xs...; [to])
extend(xs; [to])
extend(x::Union{AbstractRaster,AbstractRasterStack}; to, kw...)Extend one or multiple AbstractRaster to match the area covered by all xs, or by the keyword argument to.
Keywords
to: the Raster or dims to extend to. If notokeyword is passed, the largest shared area of allxsis used.touches:trueorfalse. Whether to useToucheswrapper on the object extent. When lines need to be included in e.g. zonal statistics,trueshoudle be used.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, Plots
evenness = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :evenness)
rnge = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :range)
# Roughly cut out South America
sa_bounds = X(-88 .. -32), Y(-57 .. 13)
sa_evenness = evenness[sa_bounds...]
# Extend range to match the whole-world raster
sa_range = extend(sa_evenness; to=rnge)
plot(sa_range)
savefig("build/extend_example.png");
nothing
# output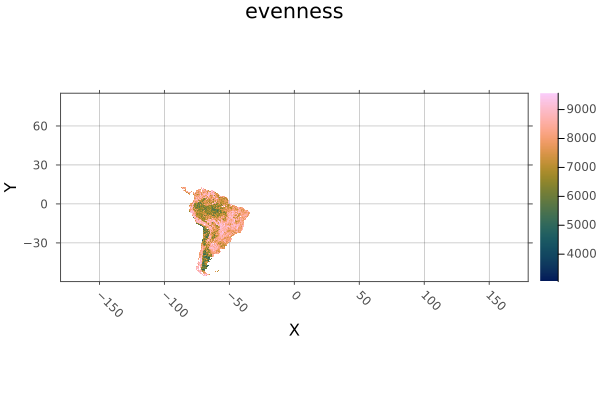
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.extract Function
extract(x, geometries; kw...)Extracts the value of Raster or RasterStack for the passed in geometries, returning an Vector{NamedTuple} with properties for :geometry and Raster or RasterStack layer values.
For lines, linestrings and linear rings points are extracted for each pixel that the line touches.
For polygons, all cells witih centers covered by the polygon are returned.
Note that if objects have more dimensions than the length of the point tuples, sliced arrays or stacks will be returned instead of single values.
Arguments
x: aRasterorRasterStackto extract values from.data: a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Keywords
geometry: include a:geometryfield in rows, which will be a tuple point. Either the original point for points or the pixel center point for line and polygon extract.trueby default.index: include:indexfield of extracted points in rows,falseby default.name: aSymbolorTupleofSymbolcorresponding to layer/s of aRasterStackto extract. All layers are extracted by default.skipmissing: skip missing points automatically.flatten: flatten extracted points from multiple geometries into a single vector.trueby default. Unmixed point geometries are always flattened. Flattening is slow and single threaded,flatten=falsemay be a large performance improvement in combination withthreaded=true.atol: a tolerance for floating point lookup values for when theLookupcontainsPoints.atolis ignored forIntervals.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.
Example
Here we extract points matching the occurrence of the Mountain Pygmy Possum, Burramis parvus. This could be used to fit a species distribution model.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, GBIF2, CSV
# Get a stack of BioClim layers, and replace missing values with `missing`
st = RasterStack(WorldClim{BioClim}, (1, 3, 5, 7, 12)) |> replace_missing
# Download some occurrence data
obs = GBIF2.occurrence_search("Burramys parvus"; limit=5, year="2009")
# use `extract` to get values for all layers at each observation point.
# We `collect` to get a `Vector` from the lazy iterator.
extract(st, obs; skipmissing=true)
# output
5-element Vector{NamedTuple{(:geometry, :bio1, :bio3, :bio5, :bio7, :bio12)}}:
(geometry = (0.21, 40.07), bio1 = 17.077084f0, bio3 = 41.20417f0, bio5 = 30.1f0, bio7 = 24.775f0, bio12 = 446.0f0)
(geometry = (0.03, 39.97), bio1 = 17.076923f0, bio3 = 39.7983f0, bio5 = 29.638462f0, bio7 = 24.153847f0, bio12 = 441.0f0)
(geometry = (0.03, 39.97), bio1 = 17.076923f0, bio3 = 39.7983f0, bio5 = 29.638462f0, bio7 = 24.153847f0, bio12 = 441.0f0)
(geometry = (0.52, 40.37), bio1 = missing, bio3 = missing, bio5 = missing, bio7 = missing, bio12 = missing)
(geometry = (0.32, 40.24), bio1 = 16.321388f0, bio3 = 41.659454f0, bio5 = 30.029825f0, bio7 = 25.544561f0, bio12 = 480.0f0)Note: passing in arrays, geometry collections or feature collections containing a mix of points and other geometries has undefined results.
sourceRasters.mappedbounds Function
mappedbounds(x)Get the bounds converted to the mappedcrs value.
Without ArchGDAL loaded, this is just the regular bounds.
sourceRasters.mappedcrs Function
mappedcrs(x)Get the mapped coordinate reference system for the Y/X dims of an array.
In Projected lookup this is used to convert Selector values form the mappedcrs defined projection to the underlying projection, and to show plot axes in the mapped projection.
In Mapped lookup this is the coordinate reference system of the index values. See setmappedcrs to set it manually.
Rasters.mappedindex Function
mappedindex(x)Get the index value of a dimension converted to the mappedcrs value.
Without ArchGDAL loaded, this is just the regular dim value.
sourceRasters.mask! Function
mask!(x; with, missingval=missingval(A))Mask A by the missing values of with, or by all values outside with if it is a polygon.
If with is a polygon, creates a new array where points falling outside the polygon have been replaced by missingval(A).
Return a new array with values of A masked by the missing values of with, or by a polygon.
Arguments
x: aRasterorRasterStack.
Keywords
with: anotherAbstractRaster, aAbstractVectorofTuplepoints, or any GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry. The coordinate reference system of the point must matchcrs(A).invert: invert the mask, so that areas no missing inwithare masked, and areas missing inwithare masked.missingval: the missing value to write to A in masked areas, by defaultmissingval(A).
Example
Mask an unmasked AWAP layer with a masked WorldClim layer, by first resampling the mask to match the size and projection.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates
# Load and plot the file
awap = read(RasterStack(AWAP, (:tmin, :tmax); date=DateTime(2001, 1, 1)))
a = plot(awap; clims=(10, 45), c=:imola)
# Create a mask my resampling a worldclim file
wc = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
wc_mask = resample(wc; to=awap)
# Mask
mask!(awap; with=wc_mask)
b = plot(awap; clims=(10, 45))
savefig(a, "build/mask_bang_example_before.png");
savefig(b, "build/mask_bang_example_after.png"); nothing
# outputBefore mask!:
After mask!:
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.mask Method
mask(A:AbstractRaster; with, missingval=missingval(A))
mask(x; with)Return a new array with values of A masked by the missing values of with, or by the shape of with, if with is a geometric object.
Arguments
x: aRasterorRasterStack
Keywords
with: anAbstractRaster, or any GeoInterface.jl compatible objects or table. The coordinate reference system of the point must matchcrs(A).invert: invert the mask, so that areas no missing inwithare masked, and areas missing inwithare masked.missingval: the missing value to use in the returned file.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.
Geometry keywords
These can be used when with is a GeoInterface.jl compatible object:
shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.
Example
Mask an unmasked AWAP layer with a masked WorldClim layer, by first resampling the mask.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates
# Load and plot the file
awap = read(Raster(AWAP, :tmax; date=DateTime(2001, 1, 1)))
a = plot(awap; clims=(10, 45))
# Create a mask my resampling a worldclim file
wc = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
wc_mask = resample(wc; to=awap)
# Mask
awap_masked = mask(awap; with=wc_mask)
b = plot(awap_masked; clims=(10, 45))
savefig(a, "build/mask_example_before.png");
savefig(b, "build/mask_example_after.png"); nothing
# outputBefore mask:
After mask:
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.missingmask Method
missingmask(obj::Raster; kw...)
missingmask(obj; [to, res, size])
missingmask(obj::RasterStack; alllayers=true, kw...)Create a mask array of missing and true values, from another Raster. AbstractRasterStack or AbstractRasterSeries are also accepted-
For AbstractRaster the default missingval is missingval(A), but others can be chosen manually.
The array returned from calling missingmask on a AbstractRaster is a Raster with the same size and fields as the original array.
Arguments
obj: aRasteror one or multiple geometries. Geometries can be a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Keywords
alllayers: iftruea mask is taken for all layers, otherwise only the first layer is used. Defaults totrueinvert: invert the mask, so that areas no missing inwithare masked, and areas missing inwithare masked.to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates
wc = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
missingmask(wc) |> plot
savefig("build/missingmask_example.png"); nothing
# output
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.missingval Function
missingval(x)Returns the value representing missing data in the dataset
sourceRasters.mosaic! Method
mosaic!(f, dest::Union{Raster,RasterStack}, regions...; kw...)
mosaic!(f, dest::Union{Raster,RasterStack}, regions; kw...)Combine regions of Raster or RasterStack into dest using the function f to combine overlapping areas.
Arguments
f: A reducing function for values whereregionsoverlap. Note that common base functions (mean,sum,prod,first,last,minimum,maximum,length) are optimised and will work on many memory or disk based files, but user-defined functions may fail at larger scales unlessopis passes as a keyword.regions: Iterable ofRasterorRasterStack. Using anAbstractArrayis usually better than aTupleor splat when there are many regions.dest: ARasterorRasterStack. May be a an opened disk-basedRaster, the result will be written to disk. With the current algorithm, the read speed is slow.
Keywords
missingval: Fills empty areas, and defaults to themissingvalof the first region.op: an operator for the reduction, e.g.add_sumforsum. For common methods likesumthese are known and detected for you, but you can provide it manually for other functions, so they continue to work at large scales.atol: Absolute tolerance for comparison between index values. This is often required due to minor differences in range values due to floating point error. It is not applied to non-float dimensions. A tuple of tolerances may be passed, matching the dimension order.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.read:readlazy raster regions before writing them. This may help if there are chunk alignment issues between the source and dest rasters.falseby default.
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.mosaic Method
mosaic(f, regions...; kw...)
mosaic(f, regions; kw...)Combine regions of Raster or RasterStack into a single object, using the function f to combine overlapping areas.
Arguments
f: A reducing function for values whereregionsoverlap. Note that common base functions (mean,sum,prod,first,last,minimum,maximum,length) are optimised and will work on many memory or disk based files, but user-defined functions may fail at larger scales unlessopis passes as a keyword.regions: Iterable ofRasterorRasterStack. Using anAbstractArrayis usually better than aTupleor splat when there are many regions.
Keywords
missingval: Fills empty areas, and defaults to themissingvalof the first region.op: an operator for the reduction, e.g.add_sumforsum. For common methods likesumthese are known and detected for you, but you can provide it manually for other functions, so they continue to work at large scales.atol: Absolute tolerance for comparison between index values. This is often required due to minor differences in range values due to floating point error. It is not applied to non-float dimensions. A tuple of tolerances may be passed, matching the dimension order.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.read:readlazy raster regions before writing them. This may help if there are chunk alignment issues between the source and dest rasters.falseby default.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.
If your mosaic has has apparent line errors, increase the atol value.
Example
Here we cut out Australia and Africa from a stack, and join them with mosaic.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, NaturalEarth, DataFrames, Dates, Plots
import ArchGDAL
countries = naturalearth("admin_0_countries", 110) |> DataFrame
climate = RasterStack(WorldClim{Climate}, (:tmin, :tmax, :prec, :wind); month=July)
country_climates = map(("Norway", "Denmark", "Sweden")) do name
country = subset(countries, :NAME => ByRow(==(name)))
trim(mask(climate; with=country); pad=10)
end
scandinavia_climate = trim(mosaic(first, country_climates; progress=false))
plot(scandinavia_climate)
savefig("build/mosaic_example_combined.png"); nothing
# outputMosaic of countries
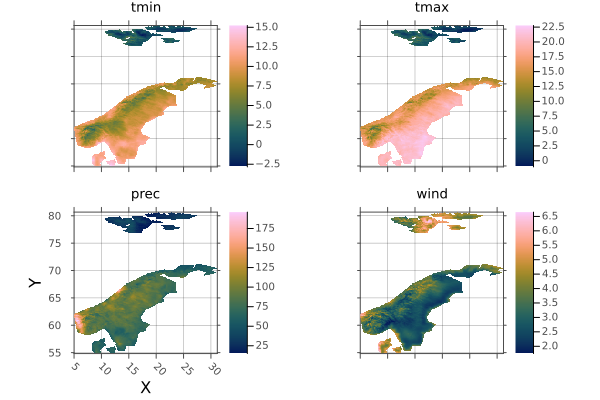
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.points Method
points(A::AbstractRaster; dims=(YDim, XDim), ignore_missing) => Array{Tuple}Returns a generator of the points in A for dimensions in dims, where points are a tuple of the values in each specified dimension index.
Keywords
dimsthe dimensions to return points from. The first slice of other layers will be used.ignore_missing: wether to ignore missing values in the array when considering points. Iftrue, all points in the dimensions will be returned, iffalseonly the points that are not=== missingval(A)will be returned.
The order of dims determines the order of the points.
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.rasterize Function
rasterize([reducer], data; geometrycolumn, kw...)Rasterize a GeoInterface.jl compatable geometry or feature, or a Tables.jl table with a :geometry column of GeoInterface.jl objects, or points columns specified by geometrycolumn
Arguments
reducer: a reducing function to reduce the fill value for all geometries that cover or touch a pixel down to a single value. The default islast. Any that takes an iterable and returns a single value will work, including custom functions. However, there are optimisations for built-in methods includingsum,first,last,minimum,maximum,extremaandStatistics.mean. These may be an order of magnitude or more faster thancountis a special-cased as it does not need a fill value.data: a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Keywords
These are detected automatically from data where possible.
fill: the value or values to fill a polygon with. ASymbolor tuple ofSymbolwill be used to retrieve properties from features or column values from table rows. An array or other iterable will be used for each geometry, in order.fillcan also be a function of the current value, e.g.x -> x + 1.op: A reducing function that accepts two values and returns one, likemintominimum. For common methods this will be assigned for you, or is not required. But you can use it instead of areduceras it will usually be faster.to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.threadsafe: specify that customreducerand/oropfunctions are thread-safe, in that the order of operation or blocking does not matter. For example,sumandmaximumare thread-safe, because the answer is approximately (besides floating point error) the same after running on nested blocks, or on all the data. In contrast,medianorlastare not, because the blocking (median) or order (last) matters.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.
Note on threading. Performance may be much better with threaded=false if reducer/op are not threadsafe. sum, prod, maximum, minimum count and mean (by combining sum and count) are threadsafe. If you know your algorithm is threadsafe, use threadsafe=true to allow all optimisations. Functions passed to fill are always threadsafe, and ignore the threadsafe argument.
Example
Rasterize a shapefile for China and plot, with a border.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates, Shapefile, Downloads
using Rasters.Lookups
# Download a borders shapefile
shapefile_url = "https://github.com/nvkelso/natural-earth-vector/raw/master/10m_cultural/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp"
shapefile_name = "country_borders.shp"
isfile(shapefile_name) || Downloads.download(shapefile_url, shapefile_name)
# Load the shapes for china
china_border = Shapefile.Handle(shapefile_name).shapes[10]
# Rasterize the border polygon
china = rasterize(last, china_border; res=0.1, missingval=0, fill=1, boundary=:touches, progress=false)
# And plot
p = plot(china; color=:spring, legend=false)
plot!(p, china_border; fillalpha=0, linewidth=0.6)
savefig("build/china_rasterized.png"); nothing
# output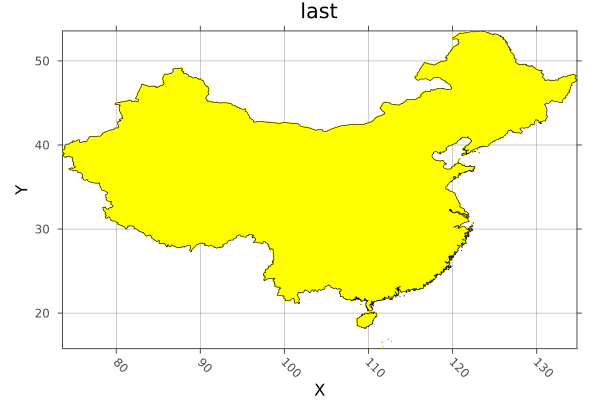
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.rasterize! Function
rasterize!([reducer], dest, data; kw...)Rasterize the geometries in data into the Raster or RasterStack dest, using the values specified by fill.
Arguments
dest: aRasterorRasterStackto rasterize into.reducer: a reducing function to reduce the fill value for all geometries that cover or touch a pixel down to a single value. The default islast. Any that takes an iterable and returns a single value will work, including custom functions. However, there are optimisations for built-in methods includingsum,first,last,minimum,maximum,extremaandStatistics.mean. These may be an order of magnitude or more faster thancountis a special-cased as it does not need a fill value.data: a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Keywords
These are detected automatically from A and data where possible.
fill: the value or values to fill a polygon with. ASymbolor tuple ofSymbolwill be used to retrieve properties from features or column values from table rows. An array or other iterable will be used for each geometry, in order.fillcan also be a function of the current value, e.g.x -> x + 1.op: A reducing function that accepts two values and returns one, likemintominimum. For common methods this will be assigned for you, or is not required. But you can use it instead of areduceras it will usually be faster.to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.threaded: run operations in parallel,falseby default. In some circumstancesthreadedcan give large speedups over single-threaded operation. This can be true for complicated geometries written into low-resolution rasters, but may not be for simple geometries with high-resolution rasters. With very large rasters threading may be counter productive due to excessive memory use. Caution should also be used:threadedshould not be used in in-place functions writing toBitArrayor other arrays where race conditions can occur.threadsafe: specify that customreducerand/oropfunctions are thread-safe, in that the order of operation or blocking does not matter. For example,sumandmaximumare thread-safe, because the answer is approximately (besides floating point error) the same after running on nested blocks, or on all the data. In contrast,medianorlastare not, because the blocking (median) or order (last) matters.to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated from the geometries, Additionally, when notoobject or anExtentis passed forto, thesizeorreskeyword must also be used.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the polygon:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insidethe polygon. The default is:center.shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:pointgeometries. using points or lines as polygons may have unexpected results.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots, Dates, Shapefile, GeoInterface, Downloads
using Rasters.Lookups
# Download a borders shapefile
shapefile_url = "https://github.com/nvkelso/natural-earth-vector/raw/master/10m_cultural/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp"
shapefile_name = "country_borders.shp"
isfile(shapefile_name) || Downloads.download(shapefile_url, shapefile_name)
# Load the shapes for indonesia
indonesia_border = Shapefile.Handle(shapefile_name).shapes[1]
# Make an empty EPSG 4326 projected Raster of the area of Indonesia
dimz = X(Projected(90.0:0.1:145; sampling=Intervals(), crs=EPSG(4326))),
Y(Projected(-15.0:0.1:10.9; sampling=Intervals(), crs=EPSG(4326)))
A = zeros(UInt32, dimz; missingval=UInt32(0))
# Rasterize each indonesian island with a different number. The islands are
# rings of a multi-polygon, so we use `GI.getring` to get them all separately.
islands = collect(GeoInterface.getring(indonesia_border))
rasterize!(last, A, islands; fill=1:length(islands), progress=false)
# And plot
p = plot(Rasters.trim(A); color=:spring)
plot!(p, indonesia_border; fillalpha=0, linewidth=0.7)
savefig("build/indonesia_rasterized.png"); nothing
# output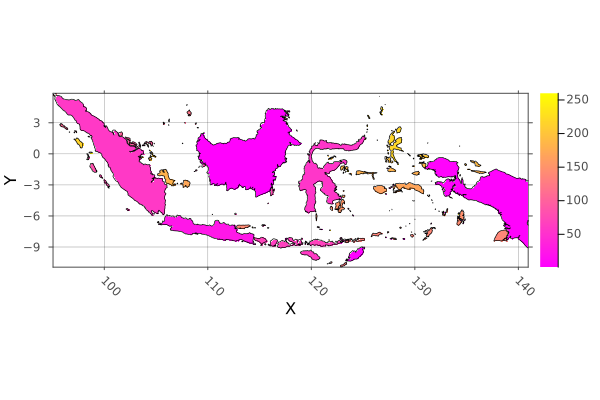
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.replace_missing Method
replace_missing(a::AbstractRaster, newmissingval)
replace_missing(a::AbstractRasterStack, newmissingval)Replace missing values in the array or stack with a new missing value, also updating the missingval field/s.
Keywords
filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL
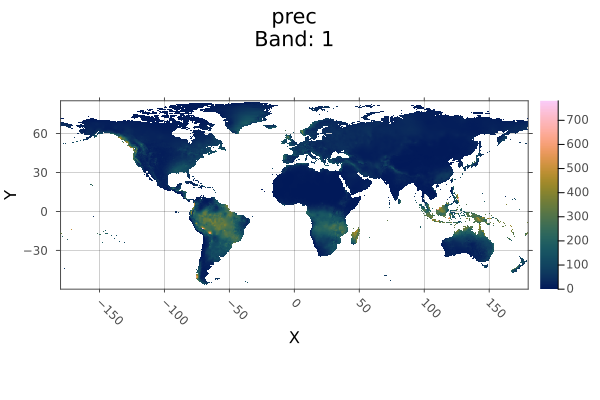
A = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1) |> replace_missing
missingval(A)
# output
missingRasters.reproject Method
reproject(source::GeoFormat, target::GeoFormat, dim::Dimension, val)reproject uses ArchGDAL.reproject, but implemented for a reprojecting a value array of values, a single dimension at a time.
Rasters.reproject Method
reproject(obj; crs)Reproject the lookups of obj to a different crs.
This is a lossless operation for the raster data, as only the lookup values change. This is only possible when the axes of source and destination projections are aligned: the change is usually from a Regular and an Irregular lookup spans.
For converting between projections that are rotated, skewed or warped in any way, use resample.
Dimensions without an AbstractProjected lookup (such as a Ti dimension) are silently returned without modification.
Arguments
obj: aLookup,Dimension,TupleofDimension,RasterorRasterStack.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.
Rasters.resample Method
resample(x; kw...)
resample(xs...; to=first(xs), kw...)resample uses warp (which uses GDALs gdalwarp) to resample a Raster or RasterStack to a new resolution and optionally new crs, or to snap to the bounds, resolution and crs of the object to.
Dimensions without an AbstractProjected lookup (such as a Ti dimension) are iteratively resampled with GDAL and joined back into a single array.
If projections can be converted for each axis independently, it may be faster and more accurate to use reproject.
Run using ArchGDAL to make this method available.
Arguments
x: the object/s to resample.
Keywords
to: aRaster,RasterStack,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extent. If notoobject is provided the extent will be calculated fromx,res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.method: ASymbolorStringspecifying the method to use for resampling. From the docs forgdalwarp::near: nearest neighbour resampling (default, fastest algorithm, worst interpolation quality).:bilinear: bilinear resampling.:cubic: cubic resampling.:cubicspline: cubic spline resampling.:lanczos: Lanczos windowed sinc resampling.:average: average resampling, computes the weighted average of all non-NODATA contributing pixels. rms root mean square / quadratic mean of all non-NODATA contributing pixels (GDAL >= 3.3):mode: mode resampling, selects the value which appears most often of all the sampled points.:max: maximum resampling, selects the maximum value from all non-NODATA contributing pixels.:min: minimum resampling, selects the minimum value from all non-NODATA contributing pixels.:med: median resampling, selects the median value of all non-NODATA contributing pixels.:q1: first quartile resampling, selects the first quartile value of all non-NODATA contributing pixels.:q3: third quartile resampling, selects the third quartile value of all non-NODATA contributing pixels.:sum: compute the weighted sum of all non-NODATA contributing pixels (since GDAL 3.1)
Where NODATA values are set to
missingval.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.
Note:
- GDAL may cause some unexpected changes in the raster, such as changing the
crstype fromEPSGtoWellKnownText(it will represent the same CRS).
Example
Resample a WorldClim layer to match an EarthEnv layer:
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, Plots
A = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
B = Raster(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, :evenness)
a = plot(A)
b = plot(resample(A; to=B))
savefig(a, "build/resample_example_before.png");
savefig(b, "build/resample_example_after.png"); nothing
# outputBefore resample:
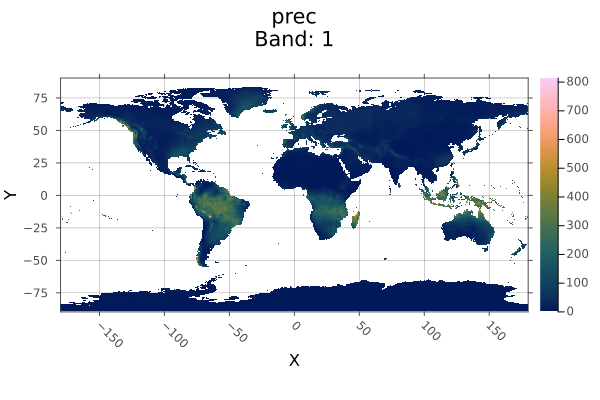
After resample:
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.setcrs Method
setcrs(x, crs)Set the crs of a Raster, RasterStack, Tuple of Dimension, or a Dimension. The crs is expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jl CRS or Mixed GeoFormat type
Rasters.setmappedcrs Method
setmappedcrs(x, crs)Set the mapped crs of a Raster, a RasterStack, a Tuple of Dimension, or a Dimension. The crs is expected to be a GeoFormatTypes.jl CRS or Mixed GeoFormat type
Rasters.slice Method
slice(A::Union{AbstractRaster,AbstractRasterStack,AbstracRasterSeries}, dims) => RasterSeriesSlice views along some dimension/s to obtain a RasterSeries of the slices.
For a Raster or RasterStack this will return a RasterSeries of Raster or RasterStack that are slices along the specified dimensions.
For a RasterSeries, the output is another series where the child objects are sliced and the series dimensions index is now of the child dimensions combined. slice on a RasterSeries with no dimensions will slice along the dimensions shared by both the series and child object.
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.trim Method
trim(x; dims::Tuple, pad::Int)Trim missingval(x) from x for axes in dims, returning a view of x.
Arguments
x: ARasterorRasterStack. For stacks, all layers must having missing values for a pixel for it to be trimmed.
Keywords
dims: By defaultdims=(XDim, YDim), so that trimming keeps the area ofXandYthat contains non-missing values along all other dimensions.pad: The trimmed size will be padded bypadon all sides, although padding will not be added beyond the original extent of the array.
As trim is lazy, filename and suffix keywords are not used.
Example
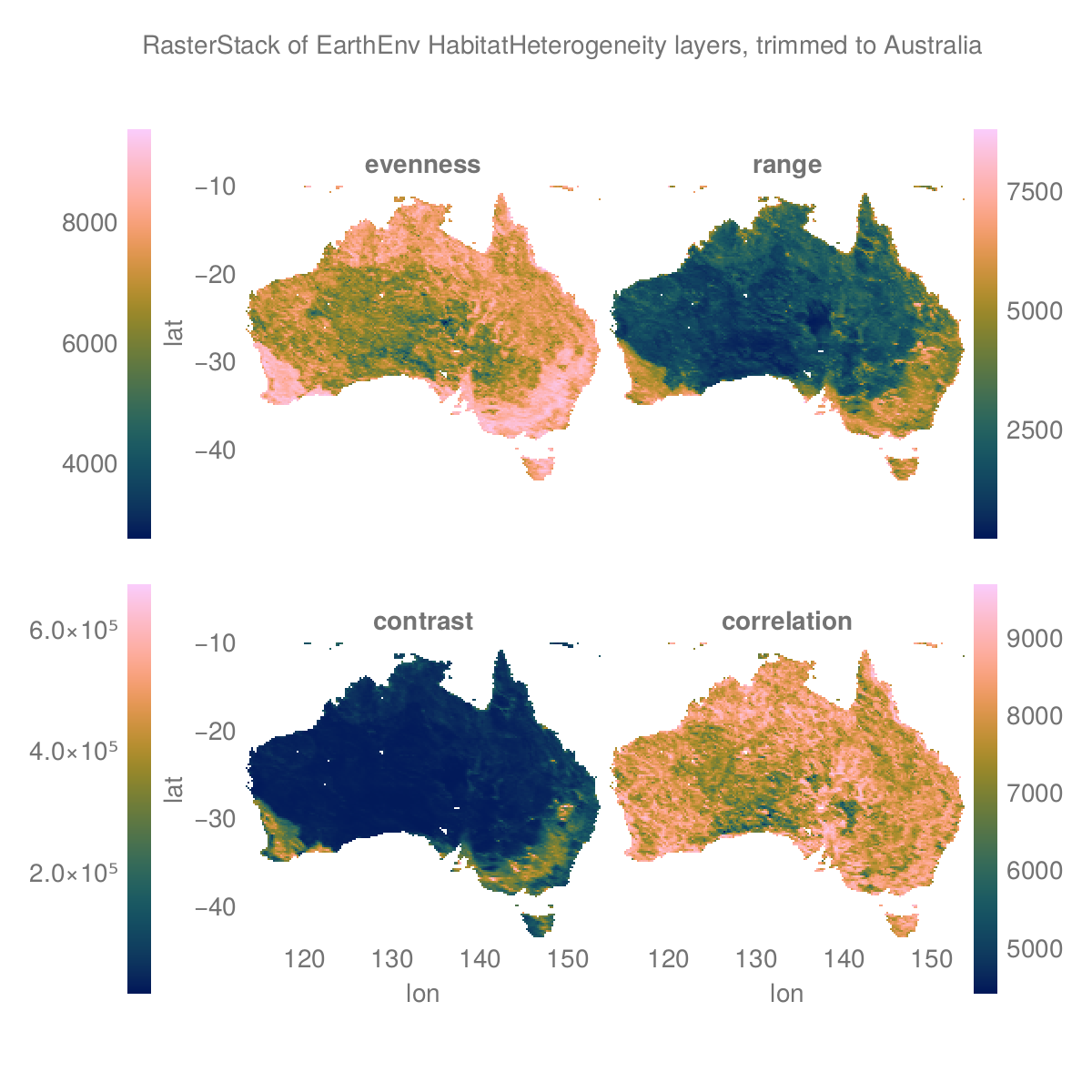
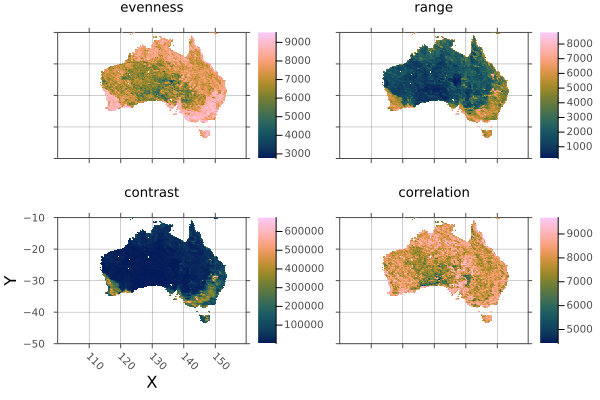
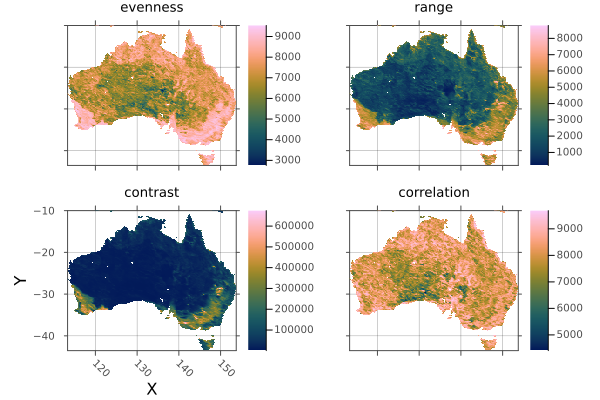
Create trimmed layers of Australian habitat heterogeneity.
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, Plots
layers = (:evenness, :range, :contrast, :correlation)
st = RasterStack(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, layers)
# Roughly cut out australia
ausbounds = X(100 .. 160), Y(-50 .. -10)
aus = st[ausbounds...]
a = plot(aus)
# Trim missing values and plot
b = plot(trim(aus))
savefig(a, "build/trim_example_before.png");
savefig(b, "build/trim_example_after.png"); nothing
# outputBefore trim:
After trim:
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.warp Method
warp(A::AbstractRaster, flags::Dict; kw...)Gives access to the GDALs gdalwarp method given a Dict of flag => value arguments that can be converted to strings, or vectors where multiple space-separated arguments are required.
Arrays with additional dimensions not handled by GDAL (other than X, Y, Band) are sliced, warped, and then combined to match the original array dimensions. These slices will not be written to disk and loaded lazily at this stage - you will need to do that manually if required.
See the gdalwarp docs for a list of arguments.
Run using ArchGDAL to make this method available.
Keywords
missingval: value representing missing data, normally detected from the file and automatically converted tomissing. Setting to an alternate value, such as0orNaNmay be desirable for improved perfomance.nothingspecifies no missing value. Using the samemissingvalthe file already has removes the overhead of replacing it, this can be done by passing themissingvalfunction asmissingval. If the file has an incorrect value, we can manually define the transformation as a pair likecorrect_value => missingorcorrect_value => NaN.correct_value => correct_valuewill keep remove the overhead of changing it. Note: Whenraw=trueis set,missingvalis not changed from the value specified in the file.filename: a filename to write to directly, useful for large files.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.missingval: the missing value to use during warping, will default to `Rasters.missingval(A). Passing a pair will specify the missing value to use after warping.
Any additional keywords are passed to ArchGDAL.Dataset.
Example
This simply resamples the array with the :tr (output file resolution) and :r flags, giving us a pixelated version:
using Rasters, ArchGDAL, RasterDataSources, Plots
A = Raster(WorldClim{Climate}, :prec; month=1)
a = plot(A)
flags = Dict(
:tr => [2.0, 2.0],
:r => :near,
)
b = plot(warp(A, flags))
savefig(a, "build/warp_example_before.png");
savefig(b, "build/warp_example_after.png"); nothing
# outputBefore warp:

After warp:
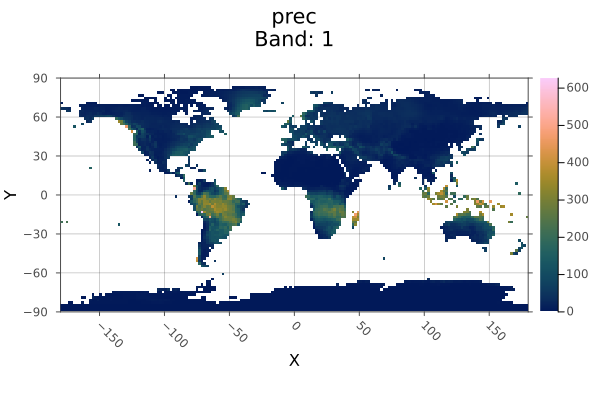
In practise, prefer resample for this. But warp may be more flexible.
WARNING: This feature is experimental. It may change in future versions, and may not be 100% reliable in all cases. Please file github issues if problems occur.
sourceRasters.zonal Method
zonal(f, x::Union{Raster,RasterStack}; of, kw...)Calculate zonal statistics for the the zone of a Raster or RasterStack covered by the of object/s.
Arguments
f: any function that reduces an iterable to a single value, such assumorStatistics.meanx: ARasterorRasterStackof: ADimTuple,Extent, aRasteror one or multiple geometries. Geometries can be a GeoInterface.jlAbstractGeometry, a nestedVectorofAbstractGeometry, or a Tables.jl compatible object containing a:geometrycolumn or points and values columns, in which casegeometrycolumnmust be specified.
Keywords
geometrycolumn:Symbolto manually select the column the geometries are in whendatais a Tables.jl compatible table, or a tuple ofSymbolfor columns of point coordinates.
These can be used when of is or contains (a) GeoInterface.jl compatible object(s):
shape: Forcedatato be treated as:polygon,:lineor:point, where possible.boundary: for polygons, include pixels where the:centeris inside the polygon, where the line:touchesthe pixel, or that are completely:insideinside the polygon. The default is:center.progress: show a progress bar,trueby default,falseto hide..skipmissing: wether to applyfto the result ofskipmissing(A)or not. Iftruefwill be passed an iterator over the values, which loses all spatial information. iffalsefwill be passes a maskedRasterorRasterStack, and will be responsible for handling missing values itself. The default value istrue.
Example
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL, DataFrames, Statistics, Dates, NaturalEarth
# Download borders
countries = naturalearth("admin_0_countries", 10) |> DataFrame
# Download and read a raster stack from WorldClim
st = RasterStack(WorldClim{Climate}; month=Jan)
# Calculate the january mean of all climate variables for all countries
january_stats = zonal(mean, st; of=countries, boundary=:touches, progress=false) |> DataFrame
# Add the country name column (natural earth has some string errors it seems)
insertcols!(january_stats, 1, :country => first.(split.(countries.ADMIN, r"[^A-Za-z ]")))
# output
258×8 DataFrame
Row │ country tmin tmax tavg prec ⋯
│ SubStrin… Float32 Float32 Float32 Float64 ⋯
─────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 │ Indonesia 21.5447 29.1865 25.3656 271.063 ⋯
2 │ Malaysia 21.3087 28.4291 24.8688 273.381
3 │ Chile 7.24534 17.9262 12.5858 78.1287
4 │ Bolivia 17.2065 27.7454 22.4758 192.542
5 │ Peru 15.0273 25.5504 20.2889 180.007 ⋯
6 │ Argentina 13.6751 27.6716 20.6732 67.1837
7 │ Dhekelia Sovereign Base Area 5.87126 15.8991 10.8868 76.25
8 │ Cyprus 5.65921 14.6665 10.1622 97.4474
⋮ │ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱
252 │ Spratly Islands 25.0 29.2 27.05 70.5 ⋯
253 │ Clipperton Island 21.5 33.2727 27.4 6.0
254 │ Macao S 11.6694 17.7288 14.6988 28.0
255 │ Ashmore and Cartier Islands NaN NaN NaN NaN
256 │ Bajo Nuevo Bank NaN NaN NaN NaN ⋯
257 │ Serranilla Bank NaN NaN NaN NaN
258 │ Scarborough Reef NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 columns and 243 rows omittedReference - Internal functions
Rasters.AbstractProjected Type
AbstractProjected <: AbstractSampledAbstract supertype for projected index lookups.
sourceRasters.FileArray Type
FileArray{S} <: DiskArrays.AbstractDiskArrayFilearray is a DiskArrays.jl AbstractDiskArray. Instead of holding an open object, it just holds a filename string that is opened lazily when it needs to be read.
Rasters.FileStack Type
FileStack{S,Na}
FileStack{S,Na}(filename, types, sizes, eachchunk, haschunks, write)A wrapper object that holds a filepath string and size/chunking metadata for a multi-layered stack stored in a single file. such as zarr or netcdf.
S is a backend type like NCDsource, and Na is a tuple of Symbol keys.
Rasters.OpenStack Type
OpenStack{X,K}
OpenStack{X,K}(dataset)A wrapper for any stack-like opened dataset that can be indexed with Symbol keys to retrieve AbstractArray layers.
OpenStack is usually hidden from users, wrapped in a regular RasterStack passed as the function argument in open(stack) when the stack is contained in a single file.
X is a backend type like NCDsource, and K is a tuple of Symbol keys.
Rasters.RasterDiskArray Type
RasterDiskArray <: DiskArrays.AbstractDiskArrayA basic DiskArrays.jl wrapper for objects that don't have one defined yet. When we open a FileArray it is replaced with a RasterDiskArray.
Rasters.Source Type
SourceAbstract type for all sources. This is used to dispatch on the source backend to use for reading a file. The source is determined by the file extension, or by the source keyword argument.
sourceBase.open Method
open(f, A::AbstractRaster; write=false)open is used to open any lazy=true AbstractRaster and do multiple operations on it in a safe way. The write keyword opens the file in write lookup so that it can be altered on disk using e.g. a broadcast.
f is a method that accepts a single argument - an Raster object which is just an AbstractRaster that holds an open disk-based object. Often it will be a do block:
lazy=false (in-memory) rasters will ignore open and pass themselves to f.
# A is an `Raster` wrapping the opened disk-based object.
open(Raster(filepath); write=true) do A
mask!(A; with=maskfile)
A[I...] .*= 2
# ... other things you need to do with the open file
endBy using a do block to open files we ensure they are always closed again after we finish working with them.
sourceBase.read! Method
read!(src::Union{AbstractString,AbstractRaster}, dst::AbstractRaster)
read!(src::Union{AbstractString,AbstractRasterStack}, dst::AbstractRasterStack)
read!(scr::AbstractRasterSeries, dst::AbstractRasterSeries)read! will copy the data from src to the object dst.
src can be an object or a file-path String.
Base.read Method
read(A::AbstractRaster)
read(A::AbstractRasterStack)
read(A::AbstractRasterSeries)read will move a Rasters.jl object completely to memory.
Keywords
checkmemory: iftrue(the default), check if there is enough memory for the operation.falsewill ignore memory needs.
Base.skipmissing Method
skipmissing(itr::Raster)Returns an iterable over the elements in a Raster object, skipping any values equal to either the missingval or missing.
Base.write Method
Base.write(filepath::AbstractString, s::AbstractRasterSeries; kw...)Write any AbstractRasterSeries to multiple files, guessing the backend from the file extension.
The lookup values of the series will be appended to the filepath (before the extension), separated by underscores.
All keywords are passed through to these Raster and RasterStack methods.
Keywords
chunks: aNTuple{N,Int}specifying the chunk size for each dimension. To specify only specific dimensions, a Tuple ofDimensionwrappingIntor aNamedTupleofIntcan be used. Other dimensions will have a chunk size of1.truecan be used to mean: use the original chunk size of the lazyRasterbeing written or X and Y of 256 by 256.falsemeans don't use chunks at all.ext: filename extension such as ".tiff" or ".nc". Used to specify specific files if only a directory path is used.force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.missingval: value representing missing data, normally detected from the file and automatically converted tomissing. Setting to an alternate value, such as0orNaNmay be desirable for improved perfomance.nothingspecifies no missing value. Using the samemissingvalthe file already has removes the overhead of replacing it, this can be done by passing themissingvalfunction asmissingval. If the file has an incorrect value, we can manually define the transformation as a pair likecorrect_value => missingorcorrect_value => NaN.correct_value => correct_valuewill keep remove the overhead of changing it. Note: Whenraw=trueis set,missingvalis not changed from the value specified in the file. For series withRasterStackchild objects, this may be aNamedTuple, one for each layer.source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.
Base.write Method
Base.write(filename::AbstractString, A::AbstractRaster; [source], kw...)Write an AbstractRaster to file, guessing the backend from the file extension or using the source keyword.
Keywords
chunks: aNTuple{N,Int}specifying the chunk size for each dimension. To specify only specific dimensions, a Tuple ofDimensionwrappingIntor aNamedTupleofIntcan be used. Other dimensions will have a chunk size of1.truecan be used to mean: use the original chunk size of the lazyRasterbeing written or X and Y of 256 by 256.falsemeans don't use chunks at all.force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.missingval: set the missing value (i.e. FillValue / nodataval) of the written raster, as Julia'smissingcannot be stored. If not passed in, an appropriatemissingvalwill be detected from the objectsmissingval, itsmetadata, or a default will be chosen base on the array element type(s).source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.
Other keyword arguments are passed to the write method for the backend.
NetCDF keywords
append: If true, the variable of the current Raster will be appended tofilename, if it actually exists.deflatelevel: Compression level:0(default) means no compression and9means maximum compression. Each chunk will be compressed individually.shuffle: Iftrue, the shuffle filter is activated which can improve the compression ratio.checksum: The checksum method can be:fletcher32or:nochecksum, the default.typename: The name of the NetCDF type required for vlen arrays (https://web.archive.org/save/https://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/netcdf/netcdf-4/newdocs/netcdf-c/nc_005fdef_005fvlen.html)
GDAL Keywords
force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.driver: A GDAL driver nameStringor a GDAL driver retrieved viaArchGDAL.getdriver(drivername). By defaultdriveris guessed from the filename extension.options::Dict{String,String}: A dictionary containing the dataset creation options passed to the driver. For example:Dict("COMPRESS" => "DEFLATE").
Valid driver names and the options for each can be found at: https://gdal.org/drivers/raster/index.html
Source comments
R grd/grid files
Write a Raster to a .grd file with a .gri header file. Returns the base of filename with a .grd extension.
GDAL (tiff, and everything else)
Used if you write a Raster with a filename extension that no other backend can write. GDAL is the fallback, and writes a lot of file types, but is not guaranteed to work.
Returns filename.
Base.write Method
Base.write(filename::AbstractString, ::Type{GRDsource}, s::AbstractRaster; kw...)Write a Raster to a .grd file with a .gri header file.
This method is called automatically if you write a Raster with a .grd or .gri extension.
Keywords
force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.
If this method is called directly the extension of filename will be ignored.
Returns the base of filename with a .grd extension.
Base.write Method
Base.write(filename::AbstractString, s::AbstractRasterStack; kw...)Write any AbstractRasterStack to one or multiple files, depending on the backend. Backend is guessed from the filename extension or forced with the source keyword.
If the source can't be saved as a stack-like object, individual array layers will be saved.
Keywords
chunks: aNTuple{N,Int}specifying the chunk size for each dimension. To specify only specific dimensions, a Tuple ofDimensionwrappingIntor aNamedTupleofIntcan be used. Other dimensions will have a chunk size of1.truecan be used to mean: use the original chunk size of the lazyRasterbeing written or X and Y of 256 by 256.falsemeans don't use chunks at all.ext: filename extension such as ".tiff" or ".nc". Used to specify specific files if only a directory path is used.force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.missingval: value representing missing data, normally detected from the file and automatically converted tomissing. Setting to an alternate value, such as0orNaNmay be desirable for improved perfomance.nothingspecifies no missing value. Using the samemissingvalthe file already has removes the overhead of replacing it, this can be done by passing themissingvalfunction asmissingval. If the file has an incorrect value, we can manually define the transformation as a pair likecorrect_value => missingorcorrect_value => NaN.correct_value => correct_valuewill keep remove the overhead of changing it. Note: Whenraw=trueis set,missingvalis not changed from the value specified in the file. ForRasterStackthis may be aNamedTuple, one for each layer.source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.suffix: a string or value to append to the filename. A tuple ofsuffixwill be applied to stack layers.keys(stack)are the default.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.
Other keyword arguments are passed to the write method for the backend.
NetCDF keywords
append: If true, the variable of the current Raster will be appended tofilename, if it actually exists.deflatelevel: Compression level:0(default) means no compression and9means maximum compression. Each chunk will be compressed individually.shuffle: Iftrue, the shuffle filter is activated which can improve the compression ratio.checksum: The checksum method can be:fletcher32or:nochecksum, the default.typename: The name of the NetCDF type required for vlen arrays (https://web.archive.org/save/https://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/netcdf/netcdf-4/newdocs/netcdf-c/nc_005fdef_005fvlen.html)
GDAL Keywords
force:falseby default. Iftrueit force writing to a file destructively, even if it already exists.driver: A GDAL driver nameStringor a GDAL driver retrieved viaArchGDAL.getdriver(drivername). By defaultdriveris guessed from the filename extension.options::Dict{String,String}: A dictionary containing the dataset creation options passed to the driver. For example:Dict("COMPRESS" => "DEFLATE").
Valid driver names and the options for each can be found at: https://gdal.org/drivers/raster/index.html
Source comments
R grd/grid files
Write a Raster to a .grd file with a .gri header file. Returns the base of filename with a .grd extension.
GDAL (tiff, and everything else)
Used if you write a Raster with a filename extension that no other backend can write. GDAL is the fallback, and writes a lot of file types, but is not guaranteed to work.
Rasters.checkmem! Method
checkmem!(x::Bool)Set checkmem to true or false.
In some architectures memory reporting may be wrong and you may wish to disable memory checks.
This setting can be overridden with the checkmem keyword, where applicable.
Rasters.create Function
create([f!], [filename], template; kw...)Create a new, uninitialised Raster or RasterStack.
If filename is a String it will be created on disk, and opened lazily. If it is nothing or not passed, an in-memory Raster will be created.
If type is a Type return value is a Raster. The eltype will usually be T, except where scale and/or offset keywords are used or a missingval of a different type is specified, in which case T will depend on the type promotion of scale, offset and missingval with T. If missingval is a Pair of on_disk_missingval => user_facing_missingval, the user facing value will effect T, not the internal on-disk value.
If types is a NamedTuple of types, the result will be a RasterStack. In this case fill and missingval can be single values (for all layers) or NamedTuple with the same names to specify per-layer.
f! will be applied to the Raster or RasterStack while it is stil open after creation, to avoid opening it twice. The return value of f! is disregarded but modifications to the Raster or the RasterStack layers will be written to disk or changed in memory.
Arguments
filename: a String file path, which will create a file on disk and return it as a lazyRaster, ornothingto create an in-memoryRaster.template: aRaster,TupleofDimensionorExtents.Extentto use as a template. If anExtentis used, asizeorreskeyword must be passed. If aTargument is not used, it is taken from thetemplateeltype.type: the element type to use in the created array. ANamedTupleof types will create aRasterStack
Keywords
name: aSymbolname for a Raster, which will also retrieve the a named layer ifRasteris used on a multi-layered file like a NetCDF.refdims:Tuple ofpositionDimensions the array was sliced from, defaulting to(). Usually not needed.metadata:DictorMetadataobject for the array, orNoMetadata().missingval: set the missing value (i.e. FillValue / nodataval) of the written raster, as Julia'smissingcannot be stored. If not passed in, an appropriatemissingvalwill be detected from the objectsmissingval, itsmetadata, or a default will be chosen base on the array element type(s).fill: A value to fill the array with, beforescaleandoffsetare applied. If there is nofill, raster values may remain undefined. They may be set tomissingvalon disk, but this is not guaranteed. It us often more efficient to usefillthan to fill manually aftercreate.source: Usually automatically detected from filepath extension. To manually force, aSymbolcan be passed:gdal,:netcdf,:grd,:grib. The internalRasters.Sourceobjects, such asRasters.GDALsource(),Rasters.GRIBsource()orRasters.NCDsource()can also be used.lazy: ABoolspecifying if to load data lazily from disk. Forcreatelazy=trueis the default, as creating a disk-based file is normally associated with it being larger than memory.chunks: aNTuple{N,Int}specifying the chunk size for each dimension. To specify only specific dimensions, a Tuple ofDimensionwrappingIntor aNamedTupleofIntcan be used. Other dimensions will have a chunk size of1.truecan be used to mean: use the original chunk size of the lazyRasterbeing written or X and Y of 256 by 256.falsemeans don't use chunks at all.scale: setscaleforx * scale + offsettransformations.offset: setoffsetforx * scale + offsettransformations.coerce: wherescaleand/oroffsetare present duringsetindex!to disk, coerce values to the element type used on dist.convertis the default, butround,truncor orceilor other functions withf(::Type{T}, x)signature may be needed where the values are not exact.verbose: whether to print messages about potential problems.trueby default.res: the resolution of the dimensions (often in meters or degrees), aRealorTuple{<:Real,<:Real}. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andsizeis not used.size: the size of the output array, as aTuple{Int,Int}or singleIntfor a square. Only required whentois not used or is anExtents.Extent, andresis not used.crs: acrswhich will be attached to the resulting raster whentonot passed or is anExtent. Otherwise the crs fromtois used.chunks: aNTuple{N,Int}specifying the chunk size for each dimension. To specify only specific dimensions, a Tuple ofDimensionwrappingIntor aNamedTupleofIntcan be used. Other dimensions will have a chunk size of1.truecan be used to mean: use the original chunk size of the lazyRasterbeing written or X and Y of 256 by 256.falsemeans don't use chunks at all.reverse_y: often we want to writeYdimensions in reverse. When building dimensions from anExtents.Extentandsizeorreswe can do this by usingreverse_y=true. Using a negative value inreswill acheive the same result. With a templateRasteror aTupleofDimension, the existing order is used.
Example
Here we create a UInt8 GeoTIFF and open it as a Raster, from -80 to 80 lattitude, and 0 to 120 longitude, with a resolution of 0.25 degrees.
We scale values from 0-1 over UInt8 0-200, and using 255. Values that don't convert exactly will error (we could use coerce=trunc to fix that).
We use UInt8(255) as the missingval on disk, but mask it with missing in the loaded Raster.
We use standard lat/lon (EPSG:4326) as the crs, and force writing if the file exists.
using Rasters, NCDatasets, ArchGDAL, Extents, Dates
using Rasters.Lookups
rast = Rasters.create("created.tif", UInt8, Extents.Extent(X=(0, 120), Y=(-80, 80), Band=(0, 12));
res=(X=10.0, Y=10.0, Band=1),
# size=(X=100, Y=100, Band=12),
name=:myraster,
crs=EPSG(4326),
force=true,
fill=0x01,
sampling=(X=Intervals(Start()), Y=Intervals(Start()), Band=Intervals(Start())),
) do A
# While we have the newly created raster open, we can write to it
A[X=1:10, Y=1:10] .= 0xff
end
read(rast)We can also create a RasterStack by passing a NamedTuple of types:
ext = Extents.Extent(X=(0, 120), Y=(-80, 80))#, Band=(1, 3))
types = (a=UInt8, b=Int32, c=Float64)
rast = Rasters.create("created.nc", types, ext;
# res=(X=1.0, Y=1.0, Band=1),
size=(X=100, Y=100),
crs=EPSG(4326),
force=true,
# sampling=(X=Intervals(Start()), Y=Intervals(Start()), Band=Points()),
end
RasterStack("created.nc")
╭───────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ 480×640 Raster{Union{Missing, Float64},2} │
├───────────────────────────────────────────┴───────────────────────────────────────── dims ┐
↓ X Projected{Float64} LinRange{Float64}(0.0, 119.75, 480) ForwardOrdered Regular Points,
→ Y Projected{Float64} LinRange{Float64}(79.75, -80.0, 640) ReverseOrdered Regular Points
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── metadata ┤
Metadata{GDALsource} of Dict{String, Any} with 2 entries:
"filepath" => "created.tif"
"scale" => 0.005
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── raster ┤
extent: Extent(X = (0.0, 119.75), Y = (-80.0, 79.75))
missingval: missing
crs: GEOGCS["WGS 84",DATUM["WGS_1984",SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199
433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AXIS["Latitude",NORTH],AXIS["Longitude",EAST],AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]
filename: nothing
└───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Rasters.rplot Method
Rasters.rplot([position::GridPosition], raster; kw...)raster may be a Raster (of 2 or 3 dimensions) or a RasterStack whose underlying rasters are 2 dimensional, or 3-dimensional with a singleton (length-1) third dimension.
Keywords
plottype = Makie.Heatmap: The type of plot. Can be any Makie plot type which accepts aRaster; in practice,Heatmap,Contour,ContourfandSurfaceare the best bets.axistype = Makie.Axis: The type of axis. This can be anAxis,Axis3,LScene, or even aGeoAxisfrom GeoMakie.jl.X = XDim: The X dimension of the raster.Y = YDim: The Y dimension of the raster.Z = YDim: The Y dimension of the raster.draw_colorbar = true: Whether to draw a colorbar for the axis or not.colorbar_position = Makie.Right(): Indicates which side of the axis the colorbar should be placed on. Can beMakie.Top(),Makie.Bottom(),Makie.Left(), orMakie.Right().colorbar_padding = Makie.automatic: The amount of padding between the colorbar and its axis. Ifautomatic, then this is set to the width of the colorbar.title = Makie.automatic: The titles of each plot. Ifautomatic, these are set to the name of the band.xlabel = Makie.automatic: The x-label for the axis. Ifautomatic, set to the dimension name of the X-dimension of the raster.ylabel = Makie.automatic: The y-label for the axis. Ifautomatic, set to the dimension name of the Y-dimension of the raster.colorbarlabel = "": Usually nothing, but here if you need it. Sets the label on the colorbar.colormap = nothing: The colormap for the heatmap. This can be set to a vector of colormaps (symbols, strings,cgrads) if plotting a 3D raster or RasterStack.colorrange = Makie.automatic: The colormap for the heatmap. This can be set to a vector of(low, high)if plotting a 3D raster or RasterStack.nan_color = :transparent: The color whichNaNvalues should take. Default to transparent.
Rasters.sample Method
Rasters.sample([rng], x, [n::Integer]; kw...)
Sample n random and optionally weighted points from from a Raster or RasterStack. Returns a Vector of NamedTuple, closely resembling the return type of extract.
Run using StatsBase to make this method available. Note that this function is not exported to avoid confusion with StatsBase.sample
Keywords
geometry: include:geometryin returnedNamedTuple. Specify the type and dimensions of the returned geometry by providing aTupleorNamedTupleof dimensions. Defaults to(X,Y)index: include:indexof theCartesianIndexin returnedNamedTuple,falseby default.name: aSymbolorTupleofSymbolcorresponding to layer/s of aRasterStackto extract. All layers by default.skipmissing: skip missing points automatically.weights: A DimArray that matches one or more of the dimensions ofxwith weights for sampling.weightstype: aStatsBase.AbstractWeightsspecifying the type of weights. Defaults toStatsBase.Weights.replace: sample with replacement,trueby default. SeeStatsBase.sampleordered: sample in order,falseby default. SeeStatsBase.sample
Example
This code draws 5 random points from a raster, weighted by cell area.
using Rasters, Rasters.Lookups, Proj, StatsBase
xdim = X(Projected(90.0:10.0:120; sampling=Intervals(Start()), crs=EPSG(4326)))
ydim = Y(Projected(0.0:10.0:50; sampling=Intervals(Start()), crs=EPSG(4326)))
myraster = rand(xdim, ydim)
Rasters.sample(myraster, 5; weights=cellarea(myraster))
# output
5-element Vector{@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}}:
@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}(((90.0, 10.0), 0.7360504790189618))
@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}(((90.0, 30.0), 0.5447657183842469))
@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}(((90.0, 30.0), 0.5447657183842469))
@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}(((90.0, 10.0), 0.7360504790189618))
@NamedTuple{geometry::Tuple{Float64, Float64}, ::Union{Missing, Float64}}(((110.0, 10.0), 0.5291143028176258))