Plotting in Makie
Plotting in Makie works somewhat differently than Plots, since the recipe system is different. You can pass a 2-D raster to any surface-like function (heatmap, contour, contourf, or even surface for a 3D plot) with ease.
2-D rasters in Makie
using CairoMakie, Makie
using Rasters, RasterDataSources, ArchGDAL
A = Raster(WorldClim{BioClim}, 5) # this is a 3D raster, so is not accepted.┌ 2160×1080 Raster{Union{Missing, Float32}, 2} bio5 ┐
├───────────────────────────────────────────────────┴──────────────────── dims ┐
↓ X Projected{Float64} -180.0:0.16666666666666666:179.83333333333331 ForwardOrdered Regular Intervals{Start},
→ Y Projected{Float64} 89.83333333333333:-0.16666666666666666:-90.0 ReverseOrdered Regular Intervals{Start}
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── metadata ┤
Metadata{Rasters.GDALsource} of Dict{String, Any} with 1 entry:
"filepath" => "./WorldClim/BioClim/wc2.1_10m_bio_5.tif"
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── raster ┤
extent: Extent(X = (-180.0, 179.99999999999997), Y = (-90.0, 90.0))
missingval: missing
crs: GEOGCS["WGS 84",DATUM["WGS_1984",SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AXIS["Latitude",NORTH],AXIS["Longitude",EAST],AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
↓ → 89.8333 89.6667 89.5 … -89.6667 -89.8333 -90.0
-180.0 missing missing missing -15.399 -13.805 -14.046
-179.833 missing missing missing -15.9605 -14.607 -14.5545
⋮ ⋱ ⋮
179.5 missing missing missing -18.2955 -16.7583 -16.72
179.667 missing missing missing -18.2847 -16.7513 -16.72
179.833 missing missing missing … -17.1478 -15.4243 -15.701fig, ax, _ = plot(A)
contour(fig[1, 2], A)
ax = Axis(fig[2, 1]; aspect = DataAspect())
contourf!(ax, A)
surface(fig[2, 2], A) # even a 3D plot work!
fig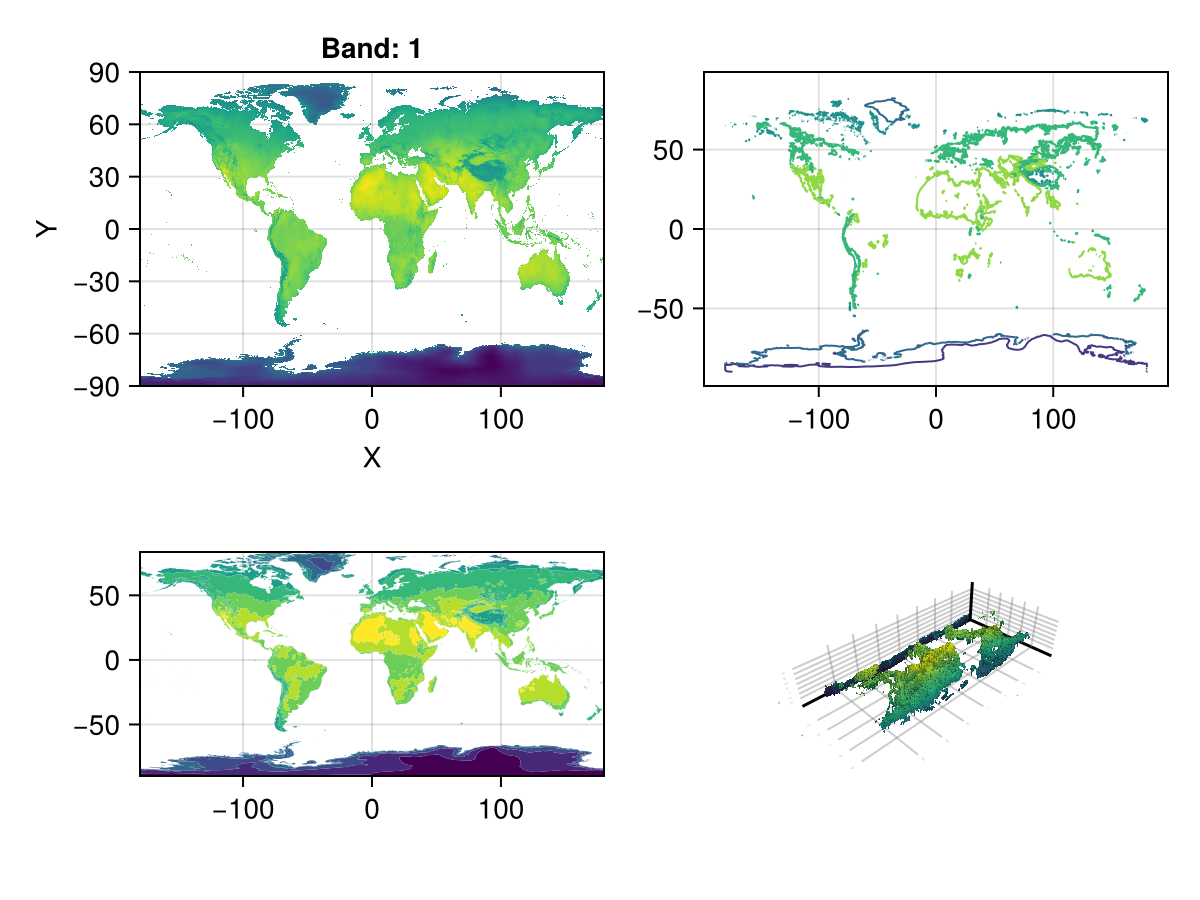
3-D rasters in Makie
Warning
This interface is experimental, and unexported for that reason. It may break at any time!
Just as in Plots, 3D rasters are treated as a series of 2D rasters, which are tiled and plotted.
You can use Rasters.rplot to visualize 3D rasters or RasterStacks in this way. An example is below:
stack = RasterStack(WorldClim{Climate}; month = 1)
Rasters.rplot(stack; Axis = (aspect = DataAspect(),),)
You can pass any theming keywords in, which are interpreted by Makie appropriately.
The plots seem a little squished here. We provide a Makie theme which makes text a little smaller and has some other space-efficient attributes:
Makie.set_theme!(Rasters.theme_rasters())
Rasters.rplot(stack)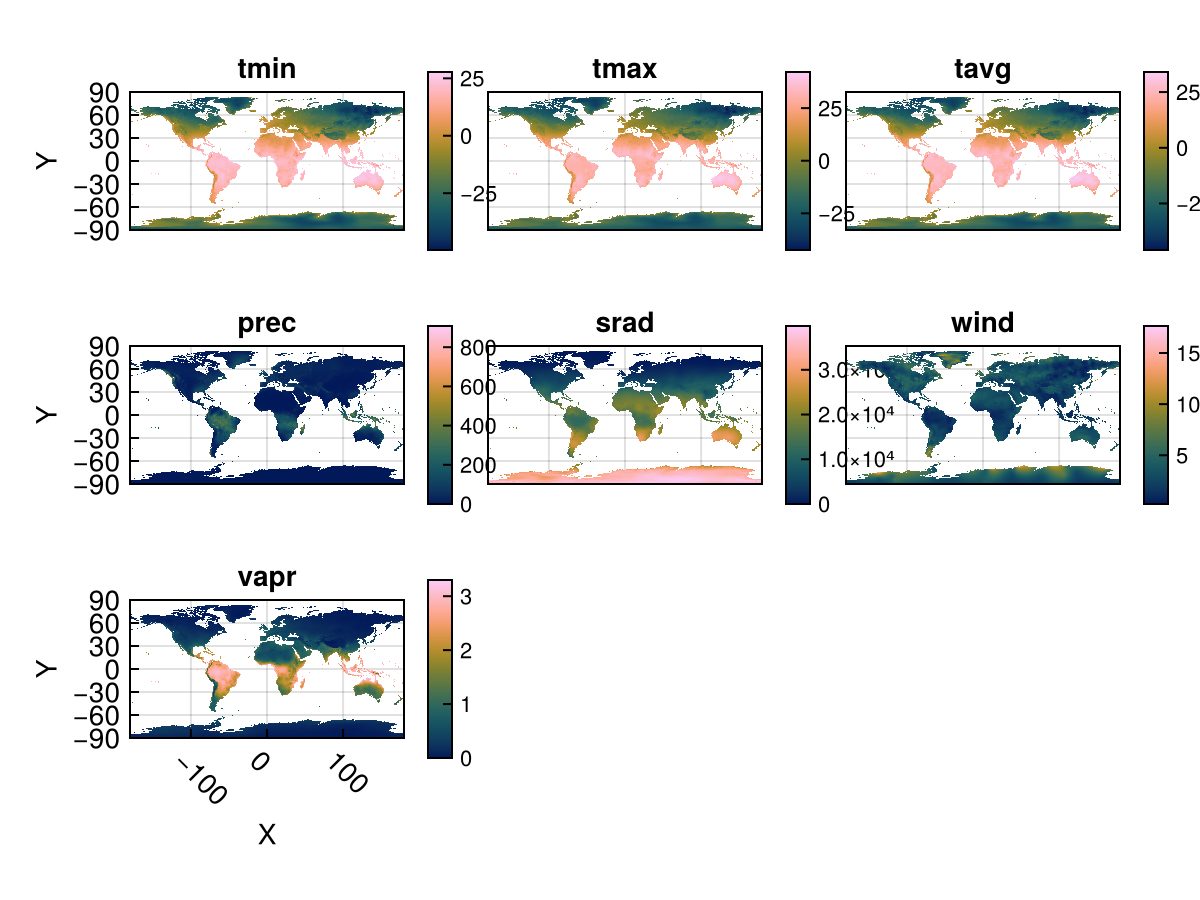
reset theme
Makie.set_theme!()Plotting with Observables, animations
Rasters.rplot should support Observable input out of the box, but the dimensions of that input must remain the same - i.e., the element names of a RasterStack must remain the same.
Makie.set_theme!(Rasters.theme_rasters())
# `stack` is the WorldClim climate data for January
stack_obs = Observable(stack)
fig = Rasters.rplot(stack_obs;
Colorbar=(; height=Relative(0.75), width=5)
)
record(fig, "rplot.mp4", 1:12; framerate = 3) do i
stack_obs[] = RasterStack(WorldClim{Climate}; month = i)
end"rplot.mp4"Makie.set_theme!() # reset themeRasters.rplot Function
Rasters.rplot([position::GridPosition], raster; kw...)raster may be a Raster (of 2 or 3 dimensions) or a RasterStack whose underlying rasters are 2 dimensional, or 3-dimensional with a singleton (length-1) third dimension.
Keywords
plottype = Makie.Heatmap: The type of plot. Can be any Makie plot type which accepts aRaster; in practice,Heatmap,Contour,ContourfandSurfaceare the best bets.axistype = Makie.Axis: The type of axis. This can be anAxis,Axis3,LScene, or even aGeoAxisfrom GeoMakie.jl.X = XDim: The X dimension of the raster.Y = YDim: The Y dimension of the raster.Z = YDim: The Y dimension of the raster.draw_colorbar = true: Whether to draw a colorbar for the axis or not.colorbar_position = Makie.Right(): Indicates which side of the axis the colorbar should be placed on. Can beMakie.Top(),Makie.Bottom(),Makie.Left(), orMakie.Right().colorbar_padding = Makie.automatic: The amount of padding between the colorbar and its axis. Ifautomatic, then this is set to the width of the colorbar.title = Makie.automatic: The titles of each plot. Ifautomatic, these are set to the name of the band.xlabel = Makie.automatic: The x-label for the axis. Ifautomatic, set to the dimension name of the X-dimension of the raster.ylabel = Makie.automatic: The y-label for the axis. Ifautomatic, set to the dimension name of the Y-dimension of the raster.colorbarlabel = "": Usually nothing, but here if you need it. Sets the label on the colorbar.colormap = nothing: The colormap for the heatmap. This can be set to a vector of colormaps (symbols, strings,cgrads) if plotting a 3D raster or RasterStack.colorrange = Makie.automatic: The colormap for the heatmap. This can be set to a vector of(low, high)if plotting a 3D raster or RasterStack.nan_color = :transparent: The color whichNaNvalues should take. Default to transparent.
Using vanilla Makie
using Rasters, RasterDataSourcesThe data
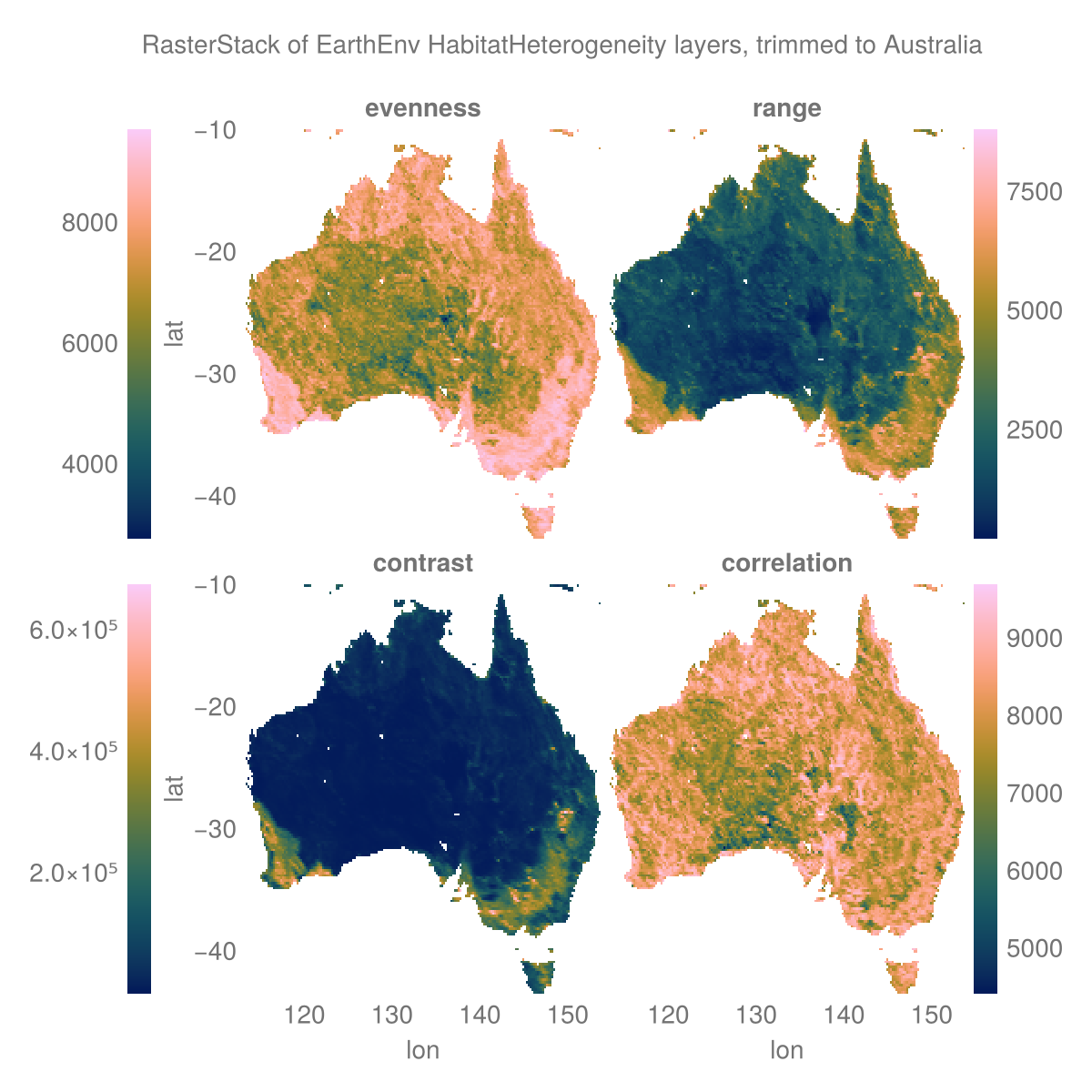
layers = (:evenness, :range, :contrast, :correlation)
st = RasterStack(EarthEnv{HabitatHeterogeneity}, layers)
ausbounds = X(100 .. 160), Y(-50 .. -10) # Roughly cut out australia
aus = st[ausbounds...] |> Rasters.trim┌ 194×161 RasterStack ┐
├─────────────────────┴────────────────────────────────────────────────── dims ┐
↓ X Projected{Float64} 113.33333333333334:0.20833333333333334:153.54166666666669 ForwardOrdered Regular Intervals{Start},
→ Y Projected{Float64} -10.208333333333334:-0.20833333333333334:-43.541666666666664 ReverseOrdered Regular Intervals{Start}
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── layers ┤
:evenness eltype: Union{Missing, UInt16} dims: X, Y size: 194×161
:range eltype: Union{Missing, UInt16} dims: X, Y size: 194×161
:contrast eltype: Union{Missing, UInt32} dims: X, Y size: 194×161
:correlation eltype: Union{Missing, UInt16} dims: X, Y size: 194×161
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────── raster ┤
extent: Extent(X = (113.33333333333334, 153.75000000000003), Y = (-43.541666666666664, -10.0))
missingval: missing
crs: GEOGCS["WGS 84",DATUM["WGS_1984",SPHEROID["WGS 84",6378137,298.257223563,AUTHORITY["EPSG","7030"]],AUTHORITY["EPSG","6326"]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0,AUTHORITY["EPSG","8901"]],UNIT["degree",0.0174532925199433,AUTHORITY["EPSG","9122"]],AXIS["Latitude",NORTH],AXIS["Longitude",EAST],AUTHORITY["EPSG","4326"]]
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘The plot
# colorbar attributes
colormap = :batlow
flipaxis = false
tickalign=1
width = 13
ticksize = 13
# figure
with_theme(theme_dark()) do
fig = Figure(; size=(600, 600), backgroundcolor=:transparent)
axs = [Axis(fig[i,j], xlabel = "lon", ylabel = "lat",
backgroundcolor=:transparent) for i in 1:2 for j in 1:2]
plt = [Makie.heatmap!(axs[i], aus[l]; colormap) for (i, l) in enumerate(layers)]
for (i, l) in enumerate(layers) axs[i].title = string(l) end
hidexdecorations!.(axs[1:2]; grid=false, ticks=false)
hideydecorations!.(axs[[2,4]]; grid=false, ticks=false)
Colorbar(fig[1, 0], plt[1]; flipaxis, tickalign, width, ticksize)
Colorbar(fig[1, 3], plt[2]; tickalign, width, ticksize)
Colorbar(fig[2, 0], plt[3]; flipaxis, tickalign, width, ticksize)
Colorbar(fig[2, 3], plt[4]; tickalign, width, ticksize)
colgap!(fig.layout, 5)
rowgap!(fig.layout, 5)
Label(fig[0, :], "RasterStack of EarthEnv HabitatHeterogeneity layers, trimmed to Australia")
fig
end
save("aus_trim.png", current_figure());CairoMakie.Screen{IMAGE}